2-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a common method of identity authentication that proves the current user is the individual who should have access to the account. Identity Verification (IDV) is a Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) solution that verifies a user’s credentials so firms know who they are engaging in a business relationship with.
This guide assimilates the use cases for both processes, identifying their key differences and establishing how they should best be used together.
What is Identity Verification?
IDV is the first process in a KYC strategy and is fundamental to businesses’ Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance obligations. Multiple methods of verifying user identity exist, and the technique employed is typically dictated by a firm’s Risk-Based Approach (RBA).
Identity Verification is becoming increasingly vital for FIs in the traditional finance (TradFi) sector and emerging financial sectors, such as Centralized Exchanges (CEXs) and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) services in the crypto industry.
The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) introduced the Customer Identification Program (CIP) in 2003. It is the pivotal first stage in a new client-business relationship that precedes Customer Due Diligence (CDD).
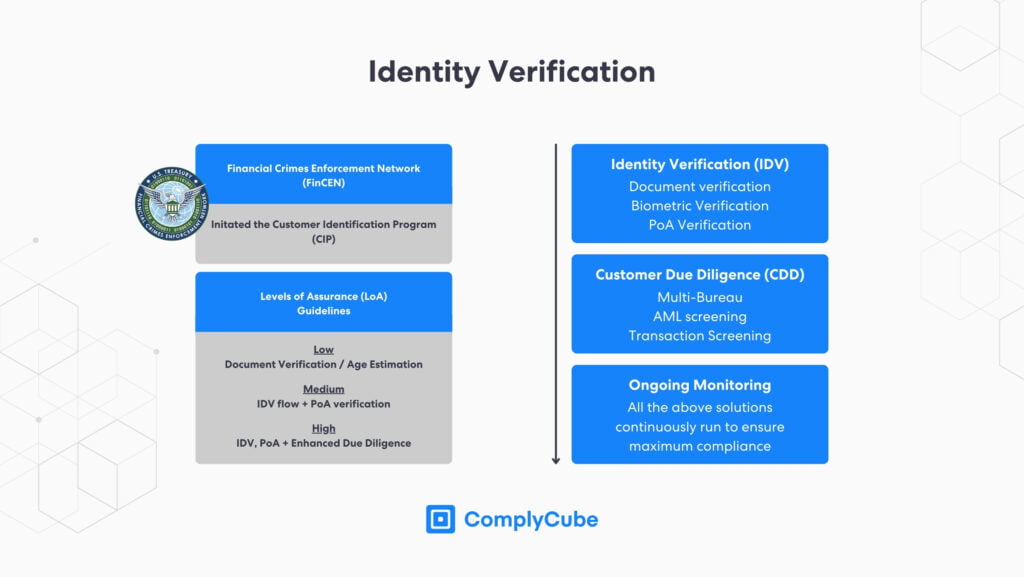
Different industries require different Levels of Assurance (LoA). For example, firms in the cryptocurrency industry require a far higher level of identity assurance than those in the e-commerce industry due to the regulatory nuances that different sectors and their regulators mandate. Digital IDV solutions, or eIDV, are fast becoming the go-to method for financial institutions due to their cost efficiency and reliability.
Document Verification
Verifying a new client’s identity starts with authenticating their KYC documents. The most common documents used are government-issued IDs, such as driver’s licenses or passports. These documents possess a national ID number and various security elements designed to make them challenging to replicate.
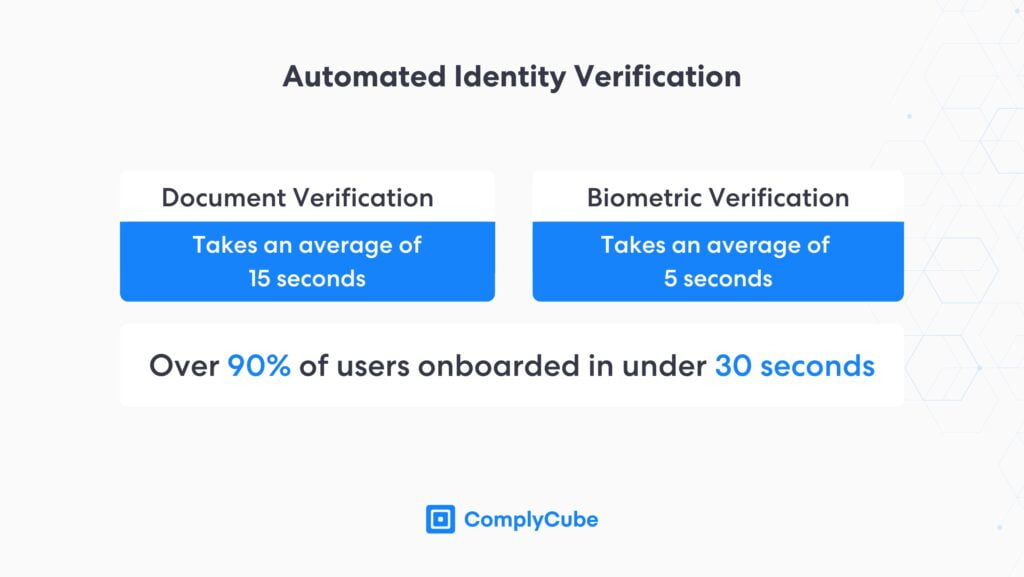
Document verification analyzes these security elements while digesting the data on the document to gain basic customer information. Modern document verification leverages advanced AI technologies to verify documents in 15 seconds, fostering a streamlined client acquisition process with limited friction.
Biometric Verification
Most Financial Institutions (FIs) use biometric verification as the next step. Biometric authentication involves matching the image in the ID provided in the document verification process against a selfie or video. Typically, this selfie or video is taken live during acquisition to create a higher LoA.
Biometric verification leverages a machine learning algorithm to verify clients in seconds alone, contributing to enhanced identity assurance. The speed at which verification is completed ensures that the customer onboarding process remains frictionless and mitigates client churn.
Proof of Address
Proof of Address (PoA) is a core IDV process. Digital PoA verification gives businesses a wealth of information beyond where a client lives. One key example is matching the document upload event’s IP address to the document’s geolocation.
This is a vital step, particularly for modern fintechs, as it ensures that users access your service from regions where your business is licensed to operate. Many cryptocurrency exchanges have received significant fines for AML breaches by permitting users to use particular services in unlicensed territories.
Hong Kong, in particular, has been cracking down on unlicensed crypto exchanges, notably against ByBit and MEXC recently. These exchanges have been charged with operating in the region without a license from the Securities and Futures Commission, the key financial regulatory force for businesses dealing with securities or security-like assets.
Address verification would be a sure methodology to ensure that exchanges only onboard clients from regions they are licensed in. For more information on the region’s crypto policies, read our guide on Hong Kong’s Crypto Regulations in 2024.

Multi-Bureau Verification
Multi-bureau verification compares the information obtained during the IDV stage against partner databases, such as credit bureaus, postal offices, and many others. These checks create an additional layer of security, as firms are informed that there is a track record of a particular user’s details.
IDV in a nutshell
Identity Verification is the process a business uses to establish that a new customer is who they say they are. IDV processes differ drastically based on varying RBAs and industry-specific compliance requirements.
- Meeting regulatory compliance obligations is critical for centralized crypto exchanges, as it enables international expansion while mitigating the possibility of AML fines.
- A DEX operating with tokenized Real World Assets (RWAs) must also initiate a CIP and IDV process if it wishes to gain compliance with local regulators.
- Decentralized crypto exchanges that provide P2P trading of cryptocurrencies do not currently require any KYC solution. As they offer seamless transfers of digital assets, there is currently no legal obligation to verify its users. This could change as the world swiftly endorses further crypto regulation.
- Typical fintech firms must also verify their users with the most stringent IDV processes, including document and biometric verification and AML monitoring.
Identity Authentication
Identity authentication is best used as an additional safeguard for accounts that have already been verified through a KYC process. It ensures that the person accessing an account at that moment is somebody who should have access. 2-factor authentication is the most common iteration of this.
Some client acquisition processes only use identity authentication; however, this process alone is not adequate to comply with rigorous financial regulations such as the Financial Action Task Force Recommendations.
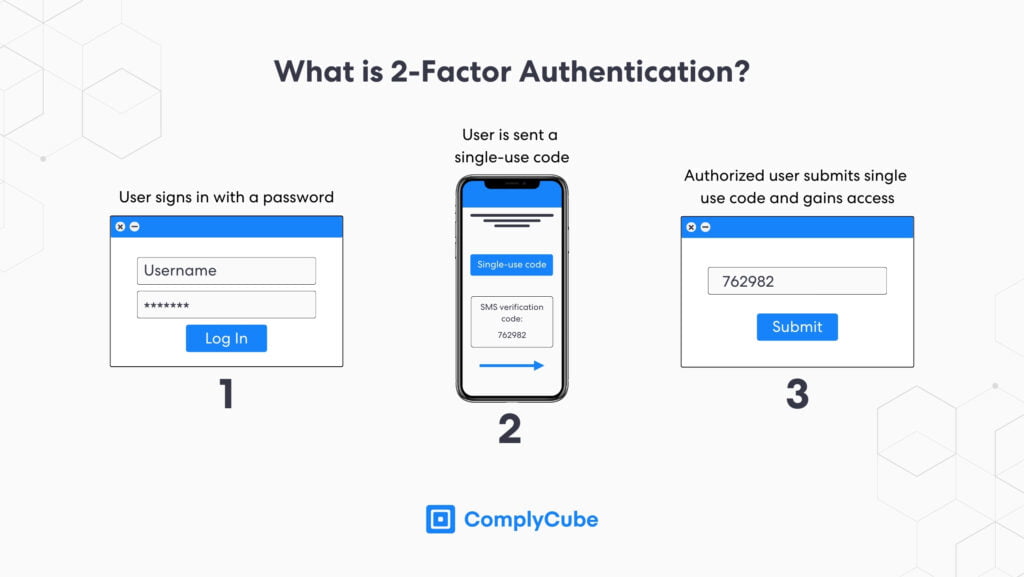
Two-Factor Authentication
2FA requires 2 different codes or sets of information before a user can access a platform. Typically, the second set of information will be requested after entering a password. 2FA can take many forms.
- Single-use email verification code
- Single-use SMS code
- Regenerative code via an authenticator app, such as Google Authenticator
- A hardware device that generates a single-use code
2FA significantly reduces the chances of an unauthorized entity or individual gaining access to an account; therefore, it is a valuable fraud prevention tool. However, it lacks the depth that Identity Verification processes provide. Furthermore, it still permits someone to fraudulently create a new account if, for example, an email account has been compromised.
Multi-Factor Authentication
This process is very similar to 2FA, however, the verification process consists of more than 2 factors, or data sets. Multi-factor authentication could consist of a password, a single-use SMS code, and a code from an authenticator app.
Biometric 2FA
Most modern smartphones are built with biometric verification capabilities. Mobile devices can use this biometric passkey as the second data set, offering the most streamlined signing-in process, as authorized users do not need to wait to gain access.
Apple stated that the likelihood of fraud or biometric failure with its Face ID technology is 1 in 1,000,000. FaceIF technology generates a great deal of security when users try to sign in again after they have verified their account with a KYC process.
Knowledge-Based Authentication
Similarly to 2FA, knowledge-based authentication uses a preset question to authenticate if a user has access to an account. These are usually basic but personal questions, including:
- What is your mother’s maiden name?
- What was the name of your first pet?
- What town/city were you born in?
This process can be iterated further using dynamic information. A banking app, for example, could be programmed to ask the user questions about the account’s recent activity and payment history, among other information only the account user would know.
Coinbase Case Study
Most CEXs use Identity Verification as part of their KYC process and identity authentication when users sign in. Together, they form a secure yet frictionless methodology for users from the point of client acquisition to returning to sign in.
Coinbase is one of the largest crypto exchanges by users and trading volume and is known as a leader in crypto compliance. The American exchange makes use of the following IDV workflow:
- Document upload
- Selfie upload
- PoA upload (if required)
Coinbase doesn’t allow individuals to use its platform without completing this program, a leading factor behind its compliance-first strategy. The exchange then leaves it up to the user’s discretion to implement a 2FA strategy.
Limitations of Identity Authentication
Identity authentication does not add any identification value to the new account that is created. If an email or SMS number has been compromised, the chance of a bad actor creating the account for malicious purposes is far higher.
Therefore, 2FA does not help prevent identity theft at the point of client acquisition and does not enable adherence to local or global Anti-Money Laundering regulations. KYC processes are pivotal for businesses that want to meet stringent and evolving regulations.
For example, many identity verification packages are paired with CDD and Ongoing Monitoring solutions, enabling a continuous risk assessment and helping firms understand which clients require Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD).
To realize the benefits of responsible technological innovation in the United States by supporting the use of new mechanisms for private sector compliance and utilizing automation and innovation to find novel ways to combat illicit finance.
Many key regulators worldwide endorse technology-based and automated compliance solutions to help fight money laundering. These include the FATF and the US Department of the Treasury, which is featured above. Financial services that employ an identity authentication process over a rigorous AML and KYC solution will likely be scrutinized by regulators in 2024 and beyond.

ComplyCube’s IDV Solutions
ComplyCube is an award-winning SaaS provider of AML and KYC solutions across a wide spectrum of sectors, including TradFi, fintech, crypto, telecoms, and many others. Firms can integrate with their infrastructure in various ways.
- Via a powerful API
- By coding their SDKs into your existing mobile tech stack
- Or using their infrastructure from the comfort of an all-in-one compliance platform.
Get in Touch with a Specialist Today
If your fintech firm or related business is looking to integrate compliance solutions that enable growth while meeting compliance requirements, get in touch with a ComplyCube specialist today to find out how they can help.