Imagine a customer applying for a loan with stellar credentials and a desire to invest quickly. Identity manipulation, including the use of synthetic identities to obtain credit, is a very common threat that often goes unperceived. In this situation, a business could suffer financial ramifications unless it takes the necessary steps, such as facial biometrics and AML screening, to ensure that the applicant is not committing synthetic identity fraud.
Synthetic identity fraud is on the rise, and traditional digital security software is no longer enough to protect businesses. Facial biometric analysis, AML risk-scoring, and other advanced fraud detection solutions can help avoid synthetic identity theft, avoiding severe financial consequences for businesses.
Unlike traditional identity theft, synthetic identities contain just enough accurate information to make them plausible, surpassing past basic level identity checking resources. Mastercard reports synthetic identity fraud stands to have cost businesses an estimated US $5 billion in 2024. As these deceitful identities are so difficult to detect, it is very common for organizations to believe their verification strategies are sufficient. Yet, data points to the very real, undeniable risks that these identities pose and their ability to surpass verification systems. As AI-driven fraud continues to gain momentum in 2025, businesses must implement the necessary defenses.
What Is a Synthetic Identity?
Synthetic identity fraud is a sophisticated but growing threat to businesses in all sectors. It occurs when a fraudster uses personally identifiable information, such as a Social Security Number (SSN) or mailing address, to create a new identity. It contains some fabricated credentials not associated with a real person that is accurate or plausible enough to bypass traditional identity theft detection software. Fraudsters use these fake digital identities to build digital footprints for fictitious people. They can, therefore, apply for a loan using a stolen SSN along with the fake identity they’ve built.
46% of organisations globally faced synthetic identity fraud in 2022.
Synthetic IDs are one of the fastest-growing tools for identity theft, used for laundering money, terrorist financing, or grand-scale theft. As many as 46% of organizations globally faced synthetic identity fraud in 2022, and that number continues to grow, costing companies exorbitant amounts of money and compromising sensitive information from unsuspecting victims.
Types of Fraudulent Identities
Fraudulent identities, also known as manufactured identities, come in numerous forms but fall into three main categories:
Fully Fictitious Identities
These have no actual verifiable information. Rather, the fraudster creates an entirely new persona with a name, address, and other data. There is no link to any other person, and the identity does not exist. These false identities can remain undetected for long periods of time. For more on fully fictitious identities, read “The Catfishing Crisis and Social Media Identity Verification.”
Identity Theft
Digital identity theft occurs when a real person’s online identity—such as login credentials, financial details, or personal information—is stolen and used without their consent. This can involve hacking into accounts, phishing scams, or data breaches to gain access to sensitive information.

Hybrid Identities (Synthetic Identity Fraud)
Synthetic identities are fabricated profiles created using a combination of real and fake information. They can include elements like a legitimate Social Security number paired with a false name or entirely invented details. These identities are used by criminals for fraud, such as opening fake accounts, obtaining credit, or committing financial crimes without detection.
Financial Losses Caused By Synthetic Identity Fraud
With fraudulent information, the bad actor can engage in one or more fraudulent practices. Some examples include:
- Opening a credit card account to apply for a loan and using their new credit and credit scores to fund nefarious activities without suspicious activity noted on the credit file for some time.
- Opening a demand deposit or checking account. One report from Aite Novarica notes that invented identities were one of the most common fraudulent activities in bank account opening in 2022.
- Applying for loans or a line of credit and using the credit to commit financial fraud. Synthetic ID fraud through loans funds illegal acts as identity thieves may use multiple synthetic identities to obtain dozens of loans.
- Evading law enforcement or regulatory detection, since the specific consumer victim often does not know what has been occurring for some time and the previous history is now noted.
- Committing fraud through online services or e-commerce platforms using a fictitious identity for phishing attempts or unexpected communications with innocent victims.
With a new credit history, thanks to the synthetic identity created, the fraudster can engage in anything that a real person with an authentic credit profile and legitimate SSN can do. They gain access to sensitive information and funds using fake names so effectively that it is extremely difficult for anyone to pinpoint the false information.
Why Synthetic Identities Are Hard to Detect
In the UK, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) mandates that all businesses in the financial service sector verify their customers before opening accounts or providing funds. Specifically, the FCA handbook states that firms should conduct electronic verification checks or PEP database inquiries and take extra provisions when common ID forms are unavailable.
That is because synthetic identities are complex and hard to detect through traditional measures. These accounts offer just enough detail to make them seem legitimate, and because fraudsters can create dozens of accounts quickly thanks to AI technology, posing a real risk. Synthetic identities often do not make a person’s records. This makes it challenging for traditional Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) systems to identify them.
Examples of Synthetic Identity Uses
Fraudsters can use synthetic identities for a wide range of fraudulent activities. Assume, for example, that an 85-year-old senior’s Social Security number is compromised. The theft could lead to a new account being opened that enables fraudsters to engage in money laundering for years to come, with no real detection, likely because of the person’s age. Address and name changes make it hard for any link to fraud to initially occur.
A criminal may develop a new identity using sophisticated AI-enabled technology that makes it highly credible. The identity may even incorporate elements such as personal preference questions. Although it represents no real person, there is enough online to make it seem authentic.
The Impact of Synthetic Identities on Businesses
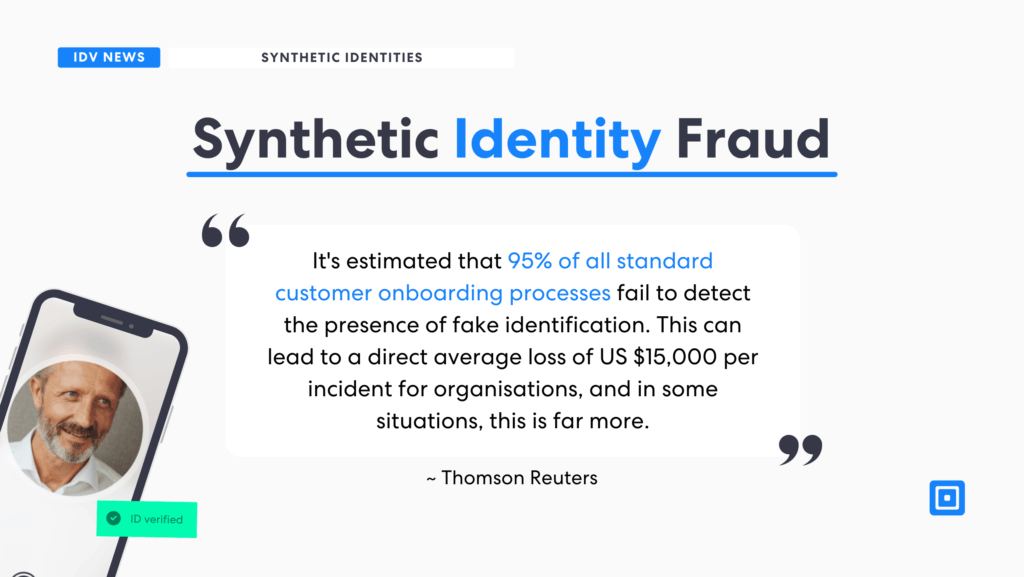
It’s estimated that 95% of all standard customer onboarding processes fail to detect the presence of fake identification. This can lead to a direct average loss of US $15,000 per incident for organizations, and in some situations, this is far more.
95% of all standard customer onboarding processes fail to detect the presence of fake identification.
Simple KYC methods do not spot these fake identities, creating a prolonged risk of loss. Yet, as the Deloitte Center for Financial Services notes, synthetic identity fraud will generate as much as $23 billion worth of cost—paid by companies themselves through various losses—by 2030.
The black market, or dark web, as it is often referred to, is one key area where fraudsters can gain access to sensitive information. The creation of synthetic identities offers lucrative rewards for bad actors, enabling these fraudsters to tap into reserves and funds directly and sell that information to more prolific criminals who could use the data to harm others, launder money from various illegal activities, and even fund terrorist activities across the globe.
By 2028, the global dark web market, which includes identity theft risks, could reach $1.3 billion, with a compound annual growth rate of 22.3%.
Dark web data is increasingly worrisome. By 2028, the global dark web market, which includes identity theft risks, could reach $1.3 billion, with a compound annual growth rate of 22.3%. A TransUnion report details just how far-reaching this type of threat is and how it impacts nearly every business today. As a whole, auto loans and the auto lending industry were projected to have been exposed to synthetic identities at a rate of $1.8 billion. The highest suspected digital fraud attempt rates in 2023 include retail at 10.6%, video gaming at 8%, and telecommunications at 5.3%. Online gaming, such as sports betting, accounted for 4.7% of the total, and financial services accounted for 4.3%.
Finding the Synthetic Identity Fraud Solution
ComplyCube offers a failsafe, a solution that eliminates the risk of such risks. The KYC solutions offered by ComplyCube eliminate the risk of non-detection of synthetic identity fraud by combining a number of highly speed tools designed to target these high-risk losses. Those solutions include:
Identity Verification (IDV): This process verifies user identities by matching biometric data and government-issued ID documents, detecting tampering or mismatches. It uses facial recognition and liveness detection to confirm identity and prevent the use of pre-recorded images or synthetic identities.
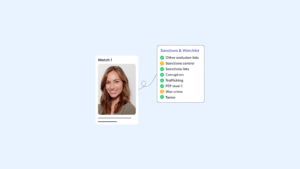
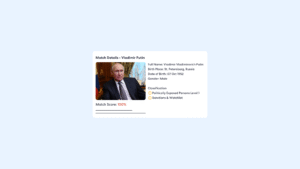
AML Screening with Continuous Monitoring: AML screening identifies unusual financial activity linked to synthetic identities by cross-referencing global watchlists. ComplyCube’s AML screening analyses various attributes to calculate a customer’s risk score, including their country, political exposure, sanction screening, adverse media mentions, and occupational risks.
Utilization of these KYC solutions reduces risk and ensures no delay in providing consumers with fast access to digital resources. ComplyCube offers advanced KYC solutions that help businesses safeguard customers and their platforms from fraudulent attempts. ComplyCube’s platform supports a company’s need to offer compliance-approved strategies to mitigate risk while still enabling companies to grow through their digital reach.
For more information on how to protect your business from fraud, reach out to one of ComplyCube’s compliance experts.