2024 has seen a global spike in digital fraud, with businesses and individuals alike facing an evolving threat that has begun to snowball out of control. AI has empowered fraudsters to create highly deceptive false identities, leveraging technologies such as deepfakes to commit sophisticated presentation attacks during customer onboarding processes, leading to often severe financial consequences. With 2025 on the horizon, what kinds of digital crime must businesses brace themselves for, and what can they do to fortify their defenses?
Several key forms of digital crime will dominate fraud attempts in the year to come, including increasingly sophisticated deepfakes, social media fraud, generative AI-led phishing attacks, compromised identities, and more. In addition, as technologies like generative AI become simpler to use, the number of bad actors continues to increase. The barrier to entry in terms of committing fraudulent attacks has substantially lowered, with tools like DeepFakeLab publicly available for anyone to create a chosen deepfake.
Sophisticated Presentation Attacks: Deepfakes
Deepfakes attacks are no longer a rare occurrence, with several tools available online that anyone can use to create one. Their prevalence online has drastically increased over the past few years, with a Deloitte reporting a 700% increase in deepfake incidents in fintech in 2023 alone.
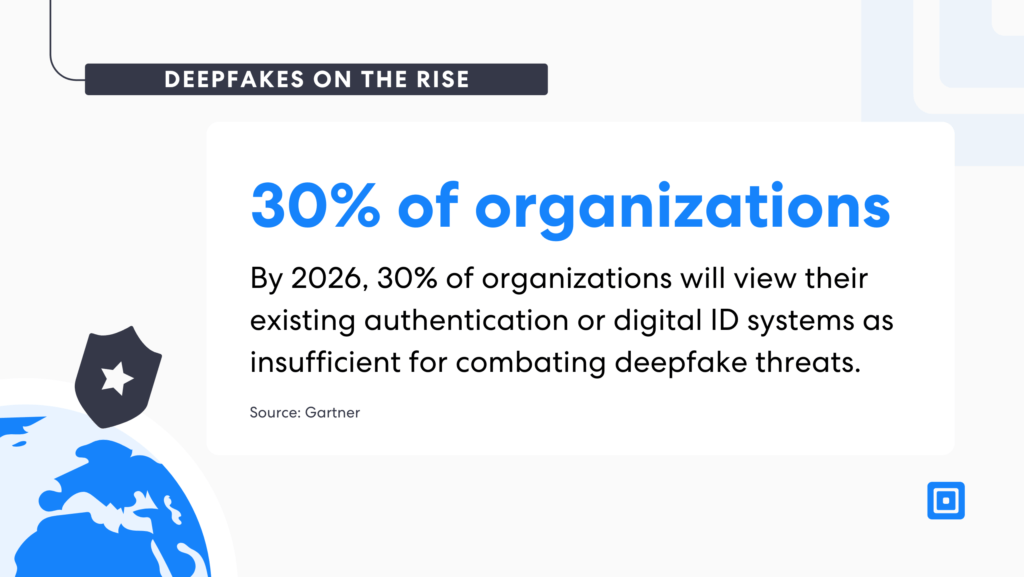
By 2026, 30% of organizations will view their existing authentication or digital ID systems as insufficient for combating deepfake threats.
A 2024 Ofcom report revealed that 60% of people in the UK have come across at least one deepfake. Additionally, Gartner predicts that by 2026, 30% of organizations will view their existing authentication or digital ID systems as insufficient for combating deepfake threats.
Akif Khan, VP Analyst at Gartner, states “In the past decade, several inflection points in fields of AI have occurred that allow for the creation of synthetic images. These artificially generated images of real people’s faces, known as deepfakes, can be used by malicious actors to undermine biometric authentication or render it inefficient,. As a result, organizations may begin to question the reliability of identity verification and authentication solutions, as they will not be able to tell whether the face of the person being verified is a live person or a deepfake.”
Humans are already often unable to differentiate a deepfake from a live person, which is why organisations must begin to heavily invest in state-of-the-art liveness detection software. Liveness detection technologies can identify deepfakes by analysing skin texture, subtle micro expressions, and more that are undetectable to the human eye or to simple identity verification processes.
Social Media Platforms As The New Playground For Cyber Crime
Beyond streamlining identity verification practices, the eID scheme also lays the foundation for a fast digital eIt’s already common knowledge that social media platforms are where many modern crimes begin, with Facebook admitting to having removed 700 million fake social media accounts in the fourth quarter of 2023, after having removed 827 million in the previous quarter. Undoubtedly, in 2025, this trend will continue as the amount of social media users continues to increase.
Generative AI tools will also enable fraudsters to carry out impersonation attacks to a higher standard, putting social media users at a higher risk of becoming victims of practices such as catfishing and pig-butchering scams. Advanced language models like Chat GPT can generate text that mimics someone’s writing style, enabling fraudsters to impersonate an individual over messages or posts. Similarly, AI can be utilised to automatically create a large number of fake accounts on social media platforms, using profiles with realistic-sounding names, pictures and backgrounds.
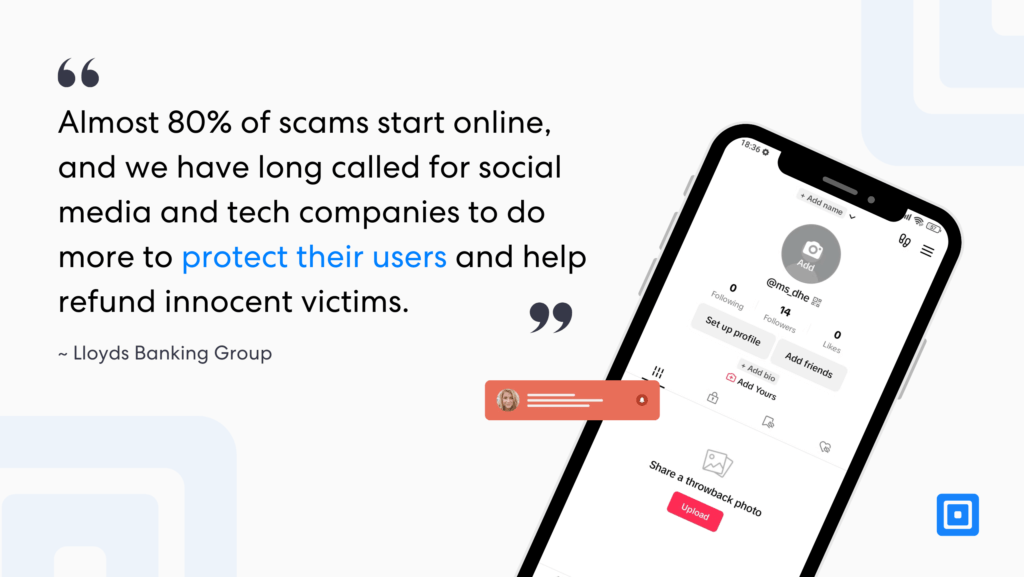
Almost 80% of scams start online.
A Lloyds spokesperson recently spoke to The Sunday Times, stating that “Almost 80% of scams start online, and we have long called for social media and tech companies to do more to protect their users and help refund innocent victims.”
So far, we have not seen social media platforms fully implement the necessary safety controls, as it couldn’t be any easier to set up an Instagram or Facebook account under a false identity. However, if these platforms were to implement tighter registration processes with proof of identity as a requirement, then fraud cases would decline.
Generative AI-Supporting Phishing Attacks
AI-enhanced phishing threats take many forms, from emails generated with flawless grammar and inclusion of personal details to highly adaptive malware that can learn and evade detection systems. This next generation of phishing attacks will leverage AI’s ability to learn from real-time data, adapting in response to evolving security measures, thus making detection even more challenging.
As well as the quality of phishing attacks increasing, the quantity of these attacks is also bound to increase with the help of generative AI. Generative AI will allow for thousands of targeted phishing attacks to be carried out simultaneously without compromising the targeted customization for maximum effect. Large-scale operations will be carried out by fraudsters, with much higher chances of success. Furthermore, as committing fraud becomes easier with the help of AI and less technical expertise is needed, more fraudsters will begin to emerge.
Research we published earlier this year showed that 60% of participants fell victim to artificial intelligence (AI)-automated phishing, which is comparable to the success rates of non-AI-phishing messages created by human experts. ~ Harvard Business Review
Harvard Business Review published research in early 2024 that highlighted the far higher success rate of AI-enhanced phishing emails, with 60% of participants falling victim to these scams. They state, “Perhaps even more worryingly, our new research demonstrates that the entire phishing process can be automated using LLMs, which reduces the costs of phishing attacks by more than 95% while achieving equal or greater success rates.” This suggests that phishing attacks will improve not just in quality but in quantity, with a vast quantity of attacks carried out worldwide across all industries.
Attacks on Supply Chains:
As we move into 2025, supply chain attacks are expected to become more sophisticated, with cybercriminals targeting smaller, less secure vendors to gain access to larger organizations. These attacks may involve AI-driven fraud, ransomware, data exfiltration, and even disrupting critical infrastructure. The National Cyber Security Centre in the UK states, “In recent years, there’s been a significant increase in the number of cyber attacks resulting from vulnerabilities within the supply chain. These attacks can result in devastating, expensive, and long-term ramifications for affected organizations, their supply chains, and their customers.”
Key Trends in Supply Chain Attacks:
- AI-Powered Attacks: Fraudsters will use AI tools to create fake communications, phishing, and deepfakes, making detection harder.
- Targeting Smaller Vendors: Cybercriminals will exploit weaker links in the supply chain to infiltrate larger organizations.
- Ransomware & Data Theft: Attackers may hold systems hostage or steal sensitive data to demand ransom.
- Disruption of Critical Infrastructure: Supply chain attacks may target sectors like energy or healthcare to cause widespread damage.
Fortifying Operations with Robust KYC
KYC (Know Your Customer) processes can be pivotal in mitigating many of the emerging digital fraud threats businesses will face in 2025, such as deepfakes, social media fraud, AI-powered phishing, and supply chain attacks.
Combating Deepfakes: KYC can strengthen identity verification by ensuring that individuals undergoing onboarding are who they claim to be. By integrating liveness detection with KYC, businesses can prevent deepfake-based fraud during account creation or financial transactions, making it harder for fraudsters to impersonate legitimate customers. For more information on the rise of deepfakes, read “Deepfake Detection Software: Preventing Fraudulent Content.“
Preventing AI-Driven Phishing: KYC data helps ensure that communications (emails, messages, etc.) involving sensitive actions, such as wire transfers or account changes, are authenticated. By verifying the identity of the individual behind each request, businesses can better identify AI-generated phishing attempts, which rely on mimicking human communication patterns.
Securing the Supply Chain: KYC can be used to verify the legitimacy of third-party vendors and suppliers, ensuring they are not linked to fraudulent or criminal activities. By performing thorough due diligence on all suppliers, businesses can reduce the risk of supply chain attacks that exploit weaker links to infiltrate larger organizations.
For more information on how to strengthen your operations with state-of-the-art KYC infrastructure, reach out to one of ComplyCube’s compliance experts today.