Cryptocurrency adoption has quickly scaled over the past few years, yet regulators didn’t take action until 2018, at which point the sector’s risks became apparent. Businesses must understand what these risks are and how a crypto scam can put them at risk of non-compliance, as crypto money laundering and other financial crimes appear to be growing globally.
Crypto money laundering poses significant challenges for regulators as well as businesses. Criminals use digital currencies like Bitcoin to launder illicit funds, transferring proceeds from illegal activities such as drug dealing and terrorism into the legitimate financial system. Through methods including mixer usage, DeFi protocols, and small transactions, bad actors hide the origins of their funds, making it difficult to trace illicit addresses.
Despite efforts by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and the United States Department, crypto crime remains a growing concern. Money laundering cases often involve criminals using crypto assets to transfer value across borders, complicating efforts to detect illicit activity and protect legitimate financial markets. Combating money laundering and terrorist financing requires ongoing collaboration between the public and private sectors. This guide will dive into how crypto enables money laundering and what businesses can do to detect and prevent crypto money laundering.
The Crypto Money Laundering Problem
Criminals laundered an estimated $2.8 billion through crypto exchanges in 2019, and the illegal activity continues to this day. Cryptocurrency exchanges are continually used to funnel illicit funds, facilitate tax evasion, and abuse the financial system, making combating money laundering a critical priority for international legal frameworks and conventions.
To meet regulatory compliance with AML legislation, cryptocurrency platforms must adhere to Financial law enforcement agencies, such as FinCEN and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in America. In order to do this, crypto exchanges must perform an AML compliance strategy, including a thorough Identity Verification (IDV), Customer Due Diligence (CDD), and ongoing monitoring, including transaction monitoring.
Understanding Cryptocurrency Money Laundering
Cryptocurrency money laundering is a complex and evolving process that involves the use of digital currencies to conceal the origin of illicit funds. This practice poses a significant concern for law enforcement agencies and financial institutions, as it can facilitate a wide range of criminal activities, including terrorist financing and proliferation financing.
The money laundering process typically involves three key stages: structuring, layering, and integration. Structuring, also known as smurfing, involves breaking down large transactions into smaller ones to avoid detection by regulatory authorities. Layering is the process of moving funds through multiple accounts or jurisdictions to obscure their origin, making it difficult for investigators to trace the money trail. Finally, integration involves incorporating the illicit funds into the legitimate financial system, often through investments or purchases that appear lawful.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have made it easier for criminals to launder money due to their high degree of anonymity and the ease with which they can be transferred across borders. However, law enforcement agencies and financial institutions are not standing idly by. They are actively combating cryptocurrency money laundering by implementing stringent anti-money laundering (AML) regulations and leveraging advanced technologies, such as blockchain analysis, to track and detect illicit transactions. These efforts are crucial in preventing the misuse of digital currencies and protecting the integrity of the financial system.
CryptoCurrency Money Laundering Cases
These processes form the basis of a rigorous Know Your Customer (KYC) strategy, which is vital when performing ongoing AML processes. Financial intelligence units (FIUs) play a crucial role in these processes, working alongside law enforcement agencies to track and prevent illicit fund flows. KYC solutions exist to bear the burden of compliance with regulatory bodies and prevent financial crime. Part of the KYC process involves verifying the legitimacy of customers’ financial accounts to prevent the storage of illicit funds.
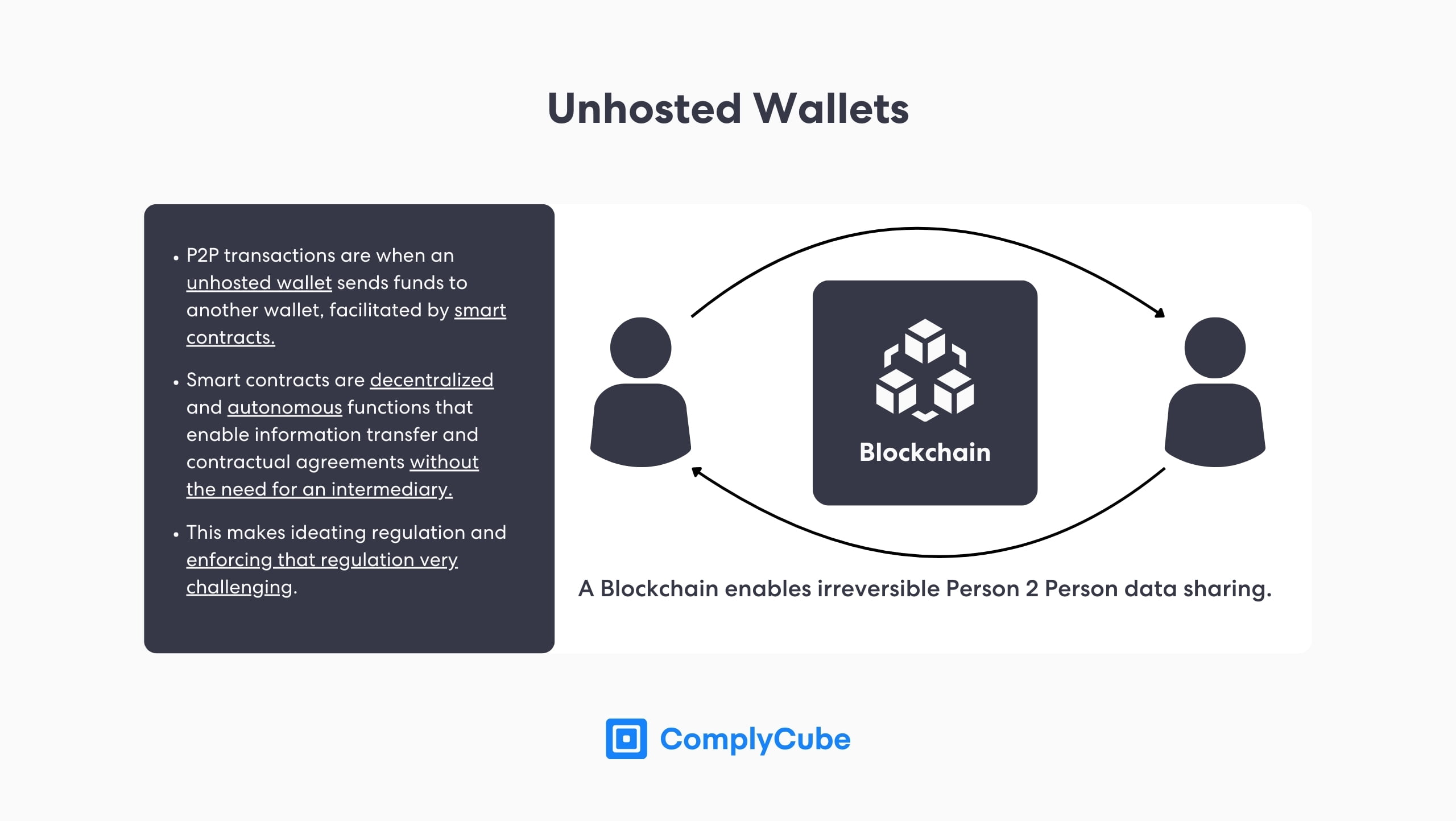
These illicit developments are creating an urgency for tighter AML and KYC requirements that comply with international standards, like the Bank Secrecy Act and FinCEN’s Travel Rule. For more information on the travel rule and crypto money laundering, read The Crypto Travel Rule: The Need for AML Compliance Software.
On July 13, British police announced they had confiscated around $250 million worth of cryptocurrency involved in an ongoing money-laundering operation. This made it one of the largest-ever crypto seizures. It followed a $160 million crypto confiscation made just three weeks prior.
Bad Actors and Crypto Crime
Compared to traditional financial institutions, cryptocurrencies are decentralized and have low barriers to entry. Their anonymous nature makes them convenient and easy to transfer across international borders, posing significant challenges to safeguarding financial systems against illicit activities.
There is good news, however. Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations are becoming more efficient in tackling this issue. Less than 1% of all crypto transactions today are estimated to relate to illegal activity, compared to 35% in 2012. A large part of that decrease has to do with businesses becoming compliant with AML regulations and learning how to spot money laundering crypto red flags.
Concentration of Money Laundering Activity
Money laundering activity is often concentrated in certain regions or countries where the regulatory environment is weak or corrupt. These areas provide a safe haven for criminals to launder their illicit funds and serve as hubs for the transfer of these funds to other parts of the world.
Several factors contribute to the concentration of money laundering activities in these regions. The lack of effective AML regulations allows criminals to operate with relative impunity. Corruption within local governments and law enforcement agencies further exacerbates the problem, creating an environment where illicit activities can thrive. Additionally, the presence of organized crime groups in these regions facilitates the laundering of money on a large scale.
Non-compliant crypto exchanges also play a significant role in this concentration. These exchanges can act as conduits for illicit funds, allowing criminals to convert their illegally gained money into digital currencies and integrate it into the legitimate financial system. By exploiting these weak points in the global financial system, money launderers can continue their operations with minimal risk of detection.
Crypto Anti-Money Laundering Policies
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and the EU now include crypto businesses in their guidelines, along with other traditional financial institutions. This means that European and non-European members alike require crypto businesses to comply with AML standards. Failure to do so could result in fines, sanctions, or jail time.
To know whether your business is affected, check if your country has transposed FATF regulations into its national laws.
Sophisticated Tactics and Techniques
Sophisticated money launderers employ a variety of advanced tactics and techniques to evade detection and obscure the origin of their illicit funds. One common method is the use of shell companies, trusts, and other complex financial structures. These entities can be used to create layers of transactions that make it difficult for investigators to trace the flow of money.
In addition to these financial structures, money launderers often use advanced technologies such as encryption and anonymization tools to conceal their identities and the origin of their funds. These technologies can make it challenging for law enforcement agencies to track and identify suspicious financial transactions.
Money launderers also employ various methods to layer and integrate their illicit funds. This can include using multiple accounts, currencies, and jurisdictions to move money around and obscure its origin. They may also use false invoices, receipts, and other documents to create a paper trail that appears legitimate.
By using these sophisticated tactics and techniques, money launderers can effectively hide their activities and integrate their illicit funds into the legitimate financial system. This makes it all the more important for financial institutions and law enforcement agencies to stay vigilant and employ advanced technologies and strategies to combat money laundering activities.
Crypto Money Laundering Red Flags to Look For
Criminals use many strategies to launder their money with cryptocurrency, the most predominant vehicle in the industry are cryptocurrency exchanges. Part of monitoring for AML red flags involves being vigilant against signs of identity theft, as it’s a prevalent method used in financial crimes to launder money. While a single red flag may not be enough to determine criminal activity, several red flags detected in combination should trigger further action.
According to the latest FATF report from 2020, here are five common red flags that crypto businesses need to look out for:
- Unusual transaction patterns
- Geographical risks
- Suspicious user profiles
- Anonymity
- Source of funds

Unusual Transaction Patterns
Irregular patterns relating to the size, frequency, or type of crypto transactions may be red flags pointing to money laundering activity, including:
- Customers making several high-value transfers within a short amount of time, such as a 24-hr period
- Structuring transaction amounts to fall below reporting thresholds
- Depositing funds into accounts with previously identified stolen currency
- Transferring crypto to service providers located in areas with low regulation standards
- Frequent large-value transfers from multiple accounts into a single account
- Immediate withdrawal of deposits without any transaction history, especially when large sums are emptied from newly opened accounts.
- Converting crypto deposits into numerous currencies with a high amount of incurred fees, even exchanging at a loss
- Converting substantial sums of fiat currency into crypto without a reasonable business premise
Geographical Risks
Criminals involved in money laundering exploit countries with weak regulations involving digital assets. So be on the lookout for:
- Crypto funds are transferred to exchanges or service providers located in regions with inadequate or non-existent AML regulations
- Customers sending or receive funds from exchanges located in other countries than the one the customer lives or operates in
- Customers that establish business addresses in countries that do not have Suspicious Activity Reports up to FATF standards
Anonymity Used to Launder Money
Cryptocurrency uses advanced technology to ensure that users and exchanges are secure from data breaches. Illicit actors often exploit cross-chain bridges for money laundering purposes, transferring and converting illicit funds across various blockchains. However, this also makes it difficult for regulators to detect fraudulent activity or which cryptocurrency transactions might contain illicit funds. Still, there are red-flag indicators that can lead investigators in the right direction:
- Customers who move funds from public blockchains to exchanges where the funds are immediately converted into privacy coins.
- Unlicensed customers who act as crypto service providers.
- Users who regularly conduct high-value transactions on peer-to-peer (P2P) crypto exchanges, especially unlicensed ones.
- Frequent or high-volume transactions on platforms that offer crypto mixing services to disguise the origin of the funds.
- Customers who frequently conduct high-value transactions on platforms that fail to comply with international standards of know-your-customer (KYC) or customer due diligence (CDD) procedures.
- Multiple transactions involving crypto ATMs, often located in areas with known financial crime risks.
- Usage of proxies or other services intended to disguise IP addresses and domain names when registering for an exchange.
Suspicious User Behaviour and Illicit Actors
Businesses should intercept customers with insufficient or forged identification documents at the KYC stage. In addition, there are different types of suspicious behavior that companies should mark as money laundering activities and red flags:
- Transactions originating from untrustworthy IP addresses or domains that differ from the country the customer operates or resides in.
- Multiple crypto wallets that are controlled by the same IP address.
- Regular use of cryptocurrencies linked to fraudulent behaviour or Ponzi schemes.
- Customers who often change their contact and identification information.
- Customers using multiple IP addresses to conduct transactions or access crypto platforms.
- Customers who often transact with the same senders or receivers, resulting in significant gains or losses, could be flagged as illicit addresses.
- Senders who do not possess a working understanding of cryptocurrency (including but not limited to the elderly) yet still conduct regular or high-value transactions.
- Customers making substantial cryptocurrency purchases beyond their established financial means.
Source of Funds
Funding sources can identify many money-laundering operations. For example, any of the following should raise a red flag:
- Funds involving accounts linked to known illicit actors and illegitimate operations such as fraud, ransomware, extortion, darknet markets, or illegal gambling sites.
- Crypto wallets connected to several credit cards that withdraw sizeable sums of fiat currency.
- Funds sourced from initial coin offerings (ICOs) that may be fraudulent, third-party mixing services, or platforms that do not comply with AML standards.
- Substantial deposits that are converted directly into privacy coins or withdrawn into a different fiat currency.
How Crypto Exchanges Can Prevent Terrorist Financing and Money Laundering Activities
What’s next once your business is familiar with the various Anti-Money Laundering (AML) red flags?
Prevention is better than a cure. Suppose a compliant exchange has implemented an appropriate risk-based approach. In that case, it’s already on the path to addressing money laundering threats by using a FATF-recommended methodology.
Additionally, any crypto business compliance program should include the following features:
- A robust CDD process to identify customers and assign them to their associated risk categories.
- Sanctions screening to ensure conformity with updated lists regarding international sanctions and politically exposed persons (PEPs).
- Adverse media monitoring of customers who feature in negative news reports.
- A powerful AI suspicious behaviour detection engine to root out bad actors.
- Cutting-edge biometric identification screening.
- Advanced linguistic and phonetic-based KYC/AML checks.
ComplyCube’s cloud SaaS platform can help Crypto businesses automate these AML and KYC workflows. It includes a flexible set of tools and APIs to address the issues listed above and offers customers a frictionless experience that builds user trust.
With cryptocurrency’s continued rise, the opportunity for criminals to misuse it will grow as well. Therefore, crypto businesses must implement a state-of-the-art KYC platform capable of handling the user verification process to shift focus back to their core business.