The crypto travel rule is a global initiative to mitigate crypto money laundering activities. It suggests that Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs), such as centralized exchanges, must share specific user data if a transaction exceeds a certain value threshold. This guide exhibits how AML compliance software is fundamental to successfully implementing this crypto compliance regulation.
The Impact of Money Laundering in the Crypto Industry
Money launderers are constantly finding new vehicles to wash their money. When bitcoin was established, and later the plethora of altcoins, bad actors pounced on this new technology. The pseudonymous nature of cryptocurrencies makes them an attractive tool for money laundering activities. Criminals can exploit these features to conceal the origins of illicit funds and transfer them across the world without leaving a trace.
This gives virtual assets unrivaled opportunities for money laundering due to their ease of use, global reach, and anonymity in transactions. Criminals can convert illicit funds into crypto assets and transfer them to crypto wallets across the globe, making it challenging for authorities to track the source and destination of the funds.
Furthermore, the cryptocurrency industry is still an emerging market, one where regulators are still comprehending the scale, size, and gravity that regulations need to be. This has left a regulatory void for financial crime to exploit.
Cryptocurrency Money Laundering Figures
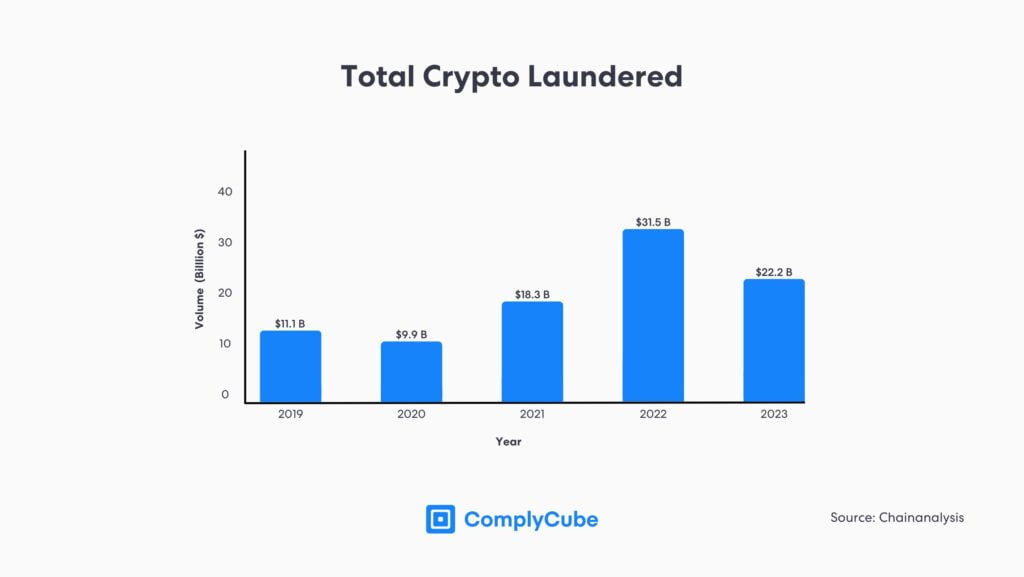
Since 2015, there has been a concerted effort to reduce illicit cryptocurrency funds traveling toward Centralized Exchanges (CEXs). This is because they are inherently less anonymous than decentralized applications (dApps).
Regulatory bodies worldwide have recognized the need to implement stringent Anti-Money Laundering (AML) measures. The Travel Rule is crucial in this effort, requiring VASPs to collect and share customer information during transactions, enabling greater transparency and accountability within the cryptocurrency industry.
Having said this, VASPs still oversaw a volume of $22.2 billion laundered via their platforms, with centralized exchanges remaining the most popular destination for fraudulent funds. This signifies that the crypto travel rule is not being implemented successfully on a local level.
The Importance of Crypto Compliance
Ensuring compliance is essential for the long-term sustainability and growth of businesses operating in the crypto space. By implementing robust crypto compliance processes, companies can establish trust with regulators, their customers, and other financial institutions.
Firms running compliance programs demonstrate a commitment to security, transparency, and ethical business practices, which are increasingly important in an industry plagued by concerns of illicit activities.
Cryptocurrency exchanges (and all crypto platforms) must take measures to mitigate terrorism financing, money laundering, and other financial crimes. Facilitating money laundering through a VASP, sometimes known as a Crypto Asset Service Provider (CASP), can result in detrimental fines and damage to the business.
Regulatory Fines
Regulatory regimes and Financial Action Task Force (FATF) style regional bodies proved in 2023 that they can and will impose significant fines on VASPs that do not comply with crypto laws. Last year, one cryptocurrency exchange was fined $4 billion for paying no heed to its platform’s ongoing money laundering activities.
If you serve US customers, you must obey US law.
This comes from Deputy Attorney General Lisa O. Monaco, signifying America’s increasingly uncompromising stance against money laundering on crypto asset service providers.
Reputational Damage
Non-compliance with policy can have devastating effects on the customer base. While crypto traders generally follow the hottest trends, fear of crypto exchanges collapsing or insolvency will cause users to churn.
Poor KYC/AML compliance strategies causing even minor reputational damage will increase regulatory probing. This will significantly reduce operational efficiency and increase expenditure on internal audits.
Expansion into New Markets
Any large-scale cryptocurrency controversy can have a significant and lasting knock-on effect on the CASP’s client base. Whether it is issues over solvency, transparency, or money laundering, ensuring the platform is optimized to prevent risk is paramount.
This is especially important when crypto institutions are expanding abroad into new markets. Cryptocurrency exchanges face stifling competition, and being the first mover in a new market can enormously impact the number of clients.
This means that firms must have the means, and thus the infrastructure, to expand into new territories with different regulatory requirements. Failing to meet crypto compliance requirements in new territories could lead to a denied license, increased regulatory probing, or sudden operation restriction.
What is the Crypto Travel Rule?
The Travel Rule, initially drafted by FinCEN (Financial Crimes Enforcement Network) and the Bank Secrecy Act, required financial services to pass on user information to the next financial institution during financial transactions. However, in 2019, the FATF recommended extending the Travel Rule to CASPs, recognizing the need to regulate the rapidly evolving crypto industry. This became known as recommendation 16.
Under the Travel Rule, crypto transactions that exceed a certain threshold (typically $1,000) must be investigated by a host of KYC (Know Your Customer) and due diligence procedures. Data about the individual conducting the transaction is shared between VASPs before the transaction can be accepted.
Crypto companies must also sanction screen the counterparty VASPs, extracting all necessary additional information to ensure both institutions are compliant with global and local regulations.
This regulatory requirement enhances transparency and prevents illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing. The Travel Rule represents a significant shift in the regulatory landscape of the crypto industry.
It requires VASPs to collect and share customer information, including the originator’s and beneficiary’s names, wallet addresses, and additional identifying details. This information enables authorities to trace the flow of funds and investigate any suspicious activities. For more information on how KYC safeguards the cryptocurrency industry, read How KYC Crypto Regulations Safeguard the Industry.
Global Regulators: The Crypto Travel Rule
The travel rule compliance requirements can differ based on regional and jurisdictional boundaries. However, the FATF suggests that the crypto travel rule should apply to all transactions exceeding $1,000.
Different regions employ the Travel Rule at different rates; this is known as the ‘sunrise issue’ and is one of the key challenges this policy faces in the VASP industry.
A report by the FATF in 2023 determined that after 4 years of adopting the travel rule for cryptocurrencies, ‘implementation is pretty poor.’
Over one third (52 of 151) have not conducted a risk assessment.
This suggests that local policymakers must regulate the industry with a firmer hand. The travel rule only works as intended if all jurisdictions adhere to it and properly implement it. This allows for seamless due diligence on users and the passing of that information to the next VASP.

Financial Institutions and Crypto Compliance: Behind Schedule
The general finding of the Financial Action Task Force was that the cryptocurrency industry was behind most other sectors regarding regulation. Their immediate guidance to companies providing services for digital assets was to introduce the travel rule thoroughly as soon as possible.
They also commented on the requirement for greater interoperability in AML services, enabling robust endorsement of the travel rule. Data malleability is something that KYC and AML services must provide as a part of their product offering.
The Financial Action Task Force: Next Steps
In H1 of 2024, the FATF is expected to publish the findings of their member jurisdictions’ employment of the travel rule. The global regulator is also presently assisting ‘low-capacity jurisdictions’ in enabling the widespread implementation of this policy.
Which Crypto Services Does the Travel Rule Apply to?
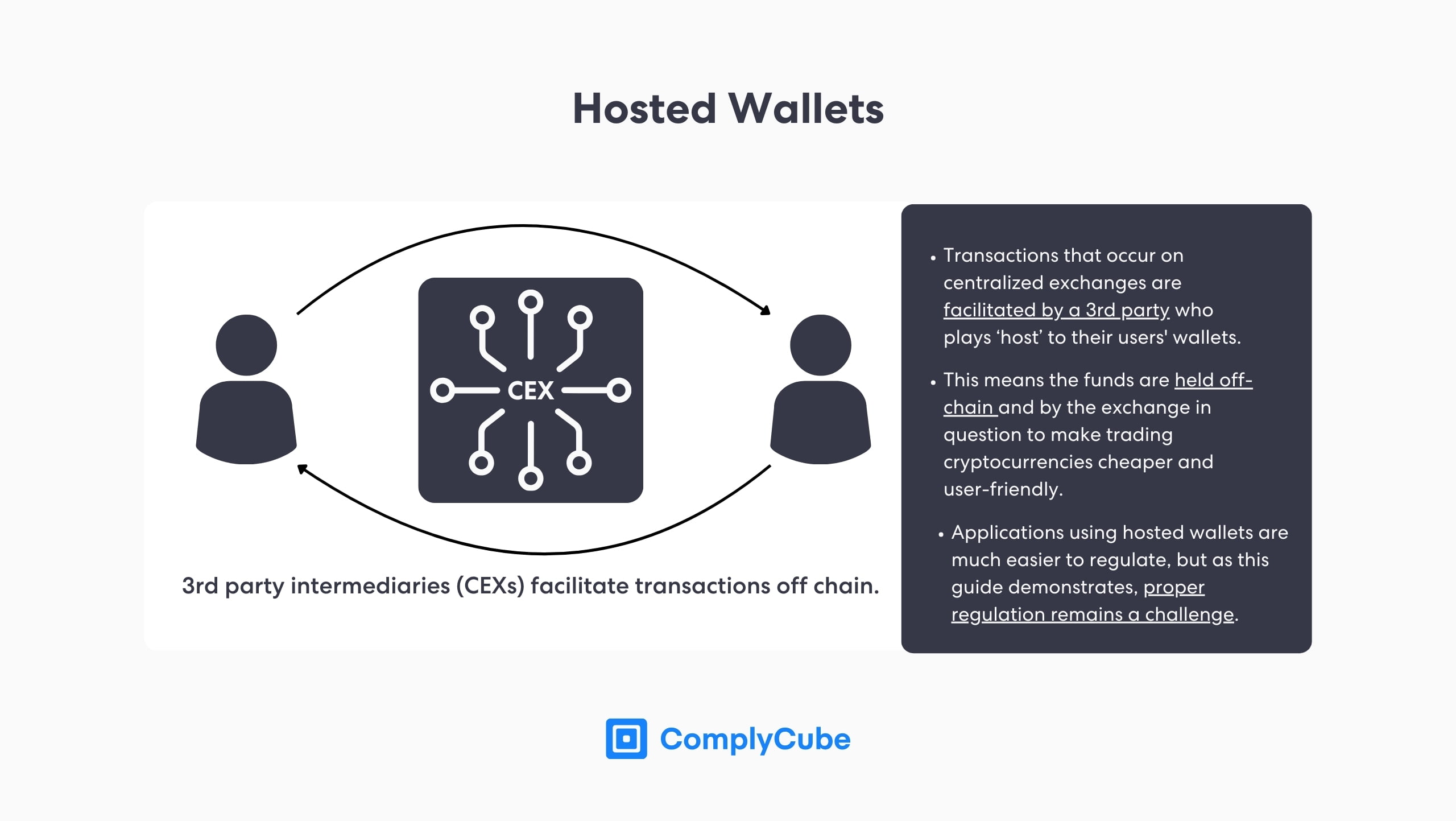
Currently, the only real platforms that have seen the successful implementation of the crypto travel rule are Centralized Exchanges. These platforms host wallets for users to buy and sell crypto without paying blockchain gas fees.
This is an easier way of buying and selling crypto and attracts more users to the industry than dApps. While these hosted wallets on exchanges are generally cheaper and easier to navigate, they come at the cost of reduced security. Cryptocurrency that users purchase is not strictly theirs until they withdraw it to an unhosted wallet.
Not Your Keys, Not Your Coins.
This saying refers to the fact that centralized exchanges have custody of users’ private keys. Private keys are the digital pass to a wallet, meaning anyone with access to these keys can access its funds. Despite the AML concerns, this is what makes unhosted wallets the favored way of holding cryptocurrency securely.
Challenges to the Crypto Travel Rule Implementation
A leading crypto money laundering policy issue is the regulation of unhosted or non-custodial wallets. These wallets, including Trust Wallet and MetaMask, are held privately by individuals, facilitating a secure method of holding cryptocurrencies on-chain.
This decentralized way of storing cryptocurrency requires no intermediary, such as crypto exchanges, to hold or trade tokens. These wallets communicate with dApps, such as Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs), staking and lending protocols, and many others.
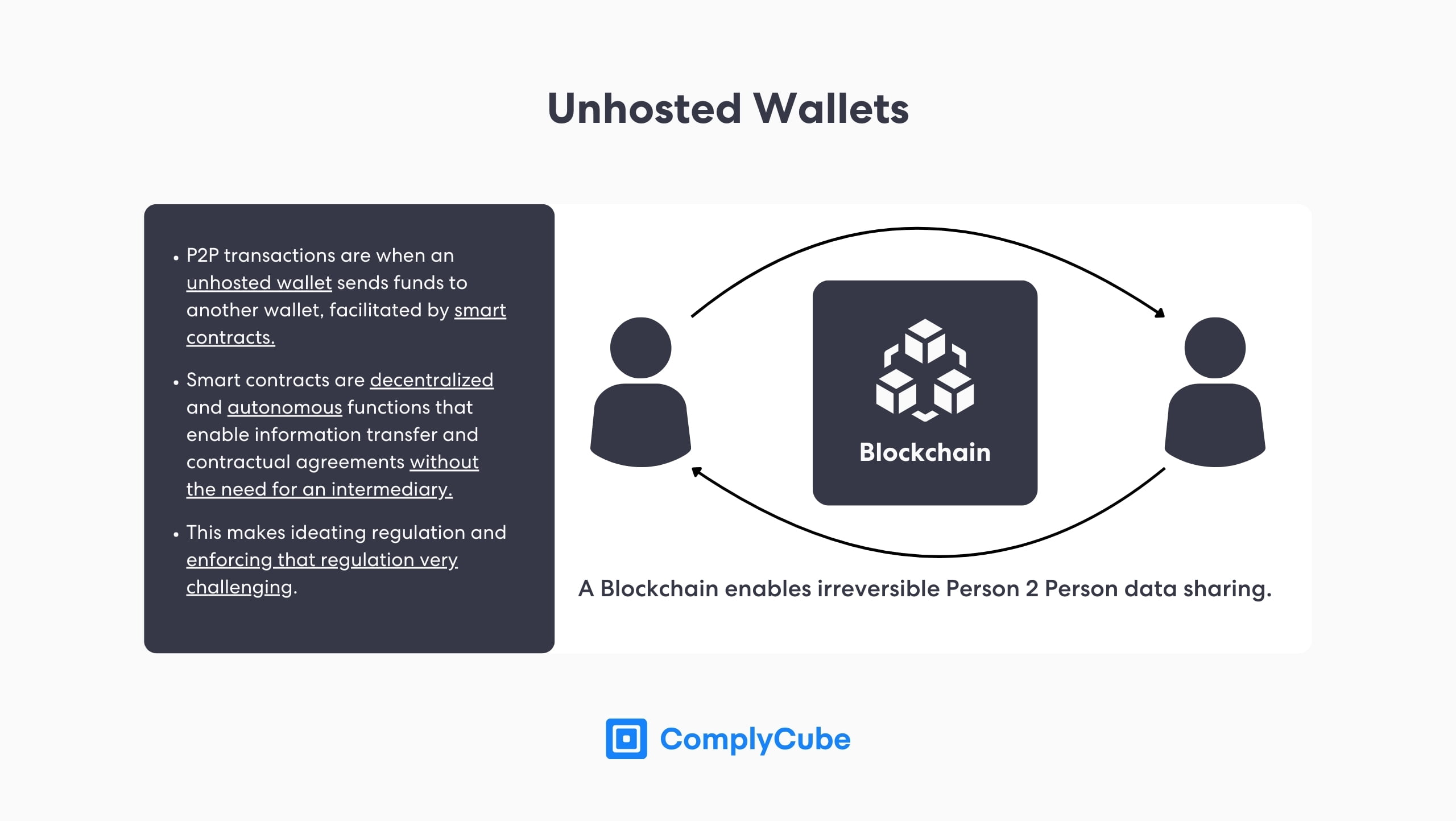
It is commonly asserted that dApps are much more complicated to enforce regulations upon, particularly the travel rule solution, because of their anonymity. Unhosted wallets require no national identity number or any beneficiary information to create. A wallet or user is only identifiable through its non-custodial wallet address, which is a series of numbers and letters.
The FATF’s report clarified that unhosted wallets, which can leverage P2P (Person-to-Person) transactions, are tricky to regulate worldwide.
Businesses that fail to comply with the crypto travel rule and other regulations could face severe penalties, regulatory sanctions, and reputational damage. Non-compliance can lead to the loss of operational licenses, hindering their ability to operate within the legal framework and access traditional financial services.
Therefore, embracing crypto compliance is crucial for businesses seeking to thrive in the rapidly evolving crypto landscape.
One of the primary challenges for VASPs when meeting the crypto travel rule requirements is the need to establish secure and efficient data-sharing mechanisms. VASPs must ensure the confidentiality and integrity of customer information while complying with regulations.
Additionally, businesses must invest in robust AML compliance software to facilitate the screening and verification of customers and counterparties. AML systems help automate the due diligence process, ensuring that businesses can identify and mitigate the risk of engaging with individuals or entities involved in illicit activities.
The Role of AML Compliance Software
AML software is pivotal in preventing illicit actors from accessing financial platforms. This enables institutions to adhere to general crypto compliance and the Travel Rule. These software solutions provide advanced risk assessment capabilities, customer screening, transaction monitoring, and regulatory reporting functionalities.
By leveraging KYC client acquisition software, businesses can streamline their AML compliance processes, reduce manual labor and mistakes, and enhance their ability to identify suspicious transactions or customers.
According to the European Union Council and Parliament, centralized exchanges now have the same obligation as banks to combat money laundering. This means that CEXs must leverage a wealth of AML, KYC, and IDV (Identity Verification) solutions that provide the flexibility to meet the growing AML requirements globally.
In the same development, the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) will now have the power to restrict or ban crypto exchanges if they are not making sufficient efforts to protect their users.
About ComplyCube
ComplyCube is swiftly becoming a go-to in the identity verification and Know Your Customer industry by providing a suite of client authentication and due diligence solutions that enable adherence to the strictest AML policies.
If your VASP is looking to strengthen its crypto travel rule compliance, or your platform faces challenges around AML, KYC, and IDV, start a conversation with us today and find out how ComplyCube’s services are shaping the security of the crypto and financial industry.