TL;DR: Biometric checks are essential for secure identity verification. This article explains how active biometrics require user interaction, how passive biometrics work in the background, and how combining both reduces fraud, ensures compliance, and improves user experience.
What is the Importance of Biometric Checks?
Biometric checks are essential for digital identity verification. As more services move online, companies must confirm who their users are. This helps stop fraud and meet strict rules, such as Know Your Customer (KYC) and Customer Due Diligence (CDD).
The COVID-19 pandemic sped up the shift to remote services. In-person identity checks became harder or even impossible. As a result, fraudsters took advantage and started using stolen IDs, fake videos, and deepfakes to trick systems.
To fight this, companies are turning to better tools. Companies House expects that 6 to 7 million people will need identity verification by the mid of November 2026. This shows how fast the demand for digital security is growing. Moreover, the Biometrics Institute stresses the need to use these tools in ways that protect privacy and earn user trust.
One of the most effective tools today is liveness detection. It helps confirm that a user is a real, live person. Businesses can choose between two main types of liveness checks: active and passive. These methods improve trust, reduce fraud, and help meet global compliance needs.
Biometric Checks Explained: What They Are and How They Work
Biometric checks use unique physical or behavioural traits to confirm a person’s identity. These traits include face, fingerprint, or voice, which are hard to forge or replicate. As such, biometrics offer a reliable layer in identity proofing and access control.
Three core terms often appear in biometric verification:
Biometric verification matches a person’s biometric data to a stored template to confirm who they are.
Biometric authentication uses that match to grant access to a service, system, or device.
Liveness detection confirms that the biometric input is coming from a real, live person, not a spoof such as a photo, video, or mask.
Biometric technologies are widely used in banking, telecom, healthcare, and government. For example, people unlock phones with facial recognition, access banking apps with fingerprints, or pass through airport gates using facial scans.
Broadly, biometric checks fall into two categories:
- Active biometrics ask users to do something such as blinking, smiling, or pressing a finger on a scanner, in a visible and intentional manner.
- Passive biometrics work silently in the background. They analyse facial cues or behaviour without asking the user to act, making them ideal for low-friction onboarding and authentication.
Both biometric types are effective, depending on the situation. Active biometrics are used in high-risk or high-assurance flows. Passive methods are better for seamless user experiences and can detect fraud in real time without causing delays. You can learn more here: “Deepfake Detection for the Modern Media Threat”.
What Are Liveness Checks?
Liveness checks verify that biometric inputs, such as a face or fingerprint, come from a real, physically present person. By analysing motion, depth, and texture, they block spoofing attempts using photos, videos, or deepfakes. Liveness detection prevents impersonation, supports compliance, and builds trust in digital onboarding and authentication.
There are two main types of liveness detection:
- Active liveness checks ask the user to complete a task and this may include blinking, smiling, turning their head, or following an on-screen prompt.
- Passive liveness checks do not require any action from the user. Instead, the system runs in the background and looks for subtle signs of life, such as depth, motion, and skin texture.
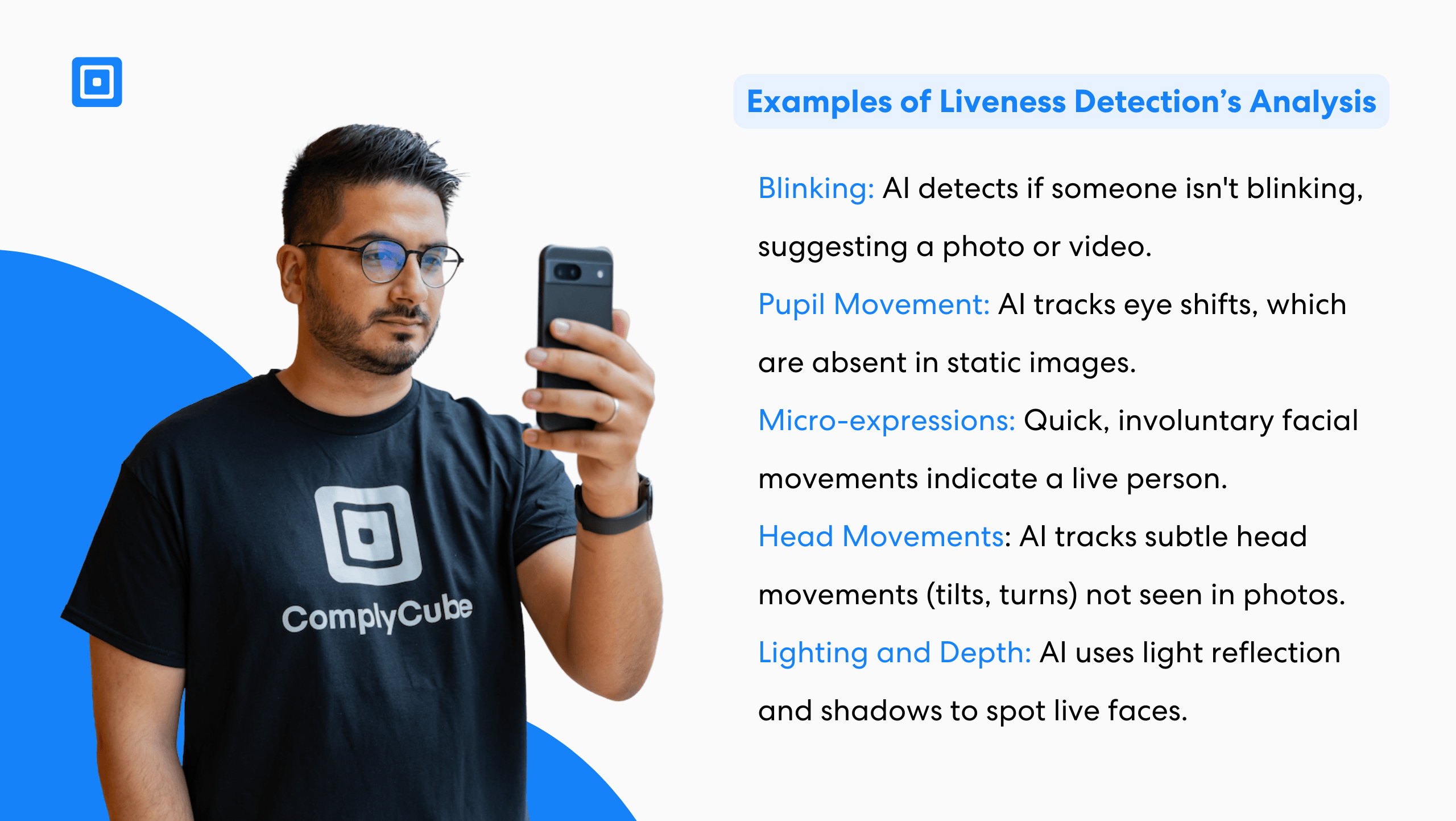
Without liveness detection, even accurate biometric matches can be fooled by fake or stolen data. These checks reduce that risk by confirming the input is live and not artificially produced. Many systems now use Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to assess facial movements, skin texture, and lighting. Some also consider behavioural cues, such as how the person holds their device.
Liveness detection can quickly identify anomalies in skin texture, lighting, and more, effectively deterring fraudsters
Harry Varatharasan, Chief Product Officer at ComplyCube, explains, “Liveness detection is a critical part of fraud prevention checks, as facial recognition processes are often impacted by non-authentic inputs, such as deepfakes. Liveness detection can quickly identify differences in skin texture, lighting, and more, effectively deterring fraudsters.”
Both methods aim to stop impersonation and identity fraud. Active checks are often used in high-risk flows where strong assurance is required. Passive checks are ideal for user journeys that need to stay fast, smooth, and low-friction. You can learn more about how liveness detection enhances biometric security here: “Liveness Detection Software for Digital Trust”.
Active Biometrics: User-Guided Identity Checks
Active biometrics ask users to perform a specific action to prove they are real and present. This action confirms that the biometric input, such as a face or fingerprint, comes from a live person and not from a static image or recording. Systems often use these checks during onboarding, account recovery, secure logins, and high-value transactions.
Direct user interaction makes active methods more resistant to spoofing. They are especially valuable in high-risk situations where a high level of identity assurance is required. Examples of active biometric checks include:
Blinking or smiling at the camera
Turning the head left or right
Following an animated dot on the screen with the eyes
Placing a finger on a scanner
Speaking a short phrase for voice recognition
These actions help systems detect signs of life and confirm that the user is who they claim to be. Active biometrics are often used alongside facial recognition or fingerprint matching. For instance, a banking app might ask the user to smile after scanning their face to ensure the image is not a static photo or pre-recorded video.
While these checks improve security, they can also introduce friction. Users must complete a task, which may cause drop-offs in low-risk scenarios. However, many users accept the added step, especially when it increases trust and protection.
Additionally, systems can be designed to use active liveness checks only when a risk signal appears, such as a login from a new device or location. This approach helps balance strong security with a smooth and user-friendly experience.
Passive Biometrics: Frictionless and Secure
Passive biometrics confirm a user’s identity by observing physical and behavioural traits. These systems work in the background and do not ask the user to do anything. They use artificial intelligence to detect natural signs that show a real person is present.
Passive systems check things like facial depth, skin texture, motion, and how the person uses their device. This makes them useful for mobile onboarding, logins, and extra security during a session. Unlike active biometrics, passive checks do not require any action. Instead, they look for natural signals such as blinking, head movement, small facial changes, typing style, or how the device is held.
These signals are hard to fake. Deepfakes and printed images usually fail to copy the tiny, real-time details that passive systems monitor. These systems also spot problems in light, depth, or motion that would not appear with a real person.
Case Study: Challenger Bank Reduces Drop-Off with Passive Biometrics
A leading European challenger bank was losing nearly 1 in 3 users during video-based identity verification due to friction from active liveness checks. After switching to ComplyCube’s passive liveness detection, the bank achieved:
- 42% boost in conversion rates
- 30-second reduction in onboarding time
- Fewer fraud attempts while staying fully EBA AML compliant
For businesses, passive biometrics offer strong security without slowing users down. They help reduce drop-off, improve satisfaction, and meet compliance needs. When combined with tools like device or location checks, they can detect risk early without interrupting trusted users.
Active vs Passive Biometric Checks: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Both active and passive biometric checks help confirm that a user is present and genuine. While they serve the same purpose, their approach, user experience, and fraud resistance differ. Selecting the right liveness detection method depends on the level of assurance required, the business risk appetite, and how much user friction is acceptable. The image below illustrates the key differences between passive and active liveness detection.
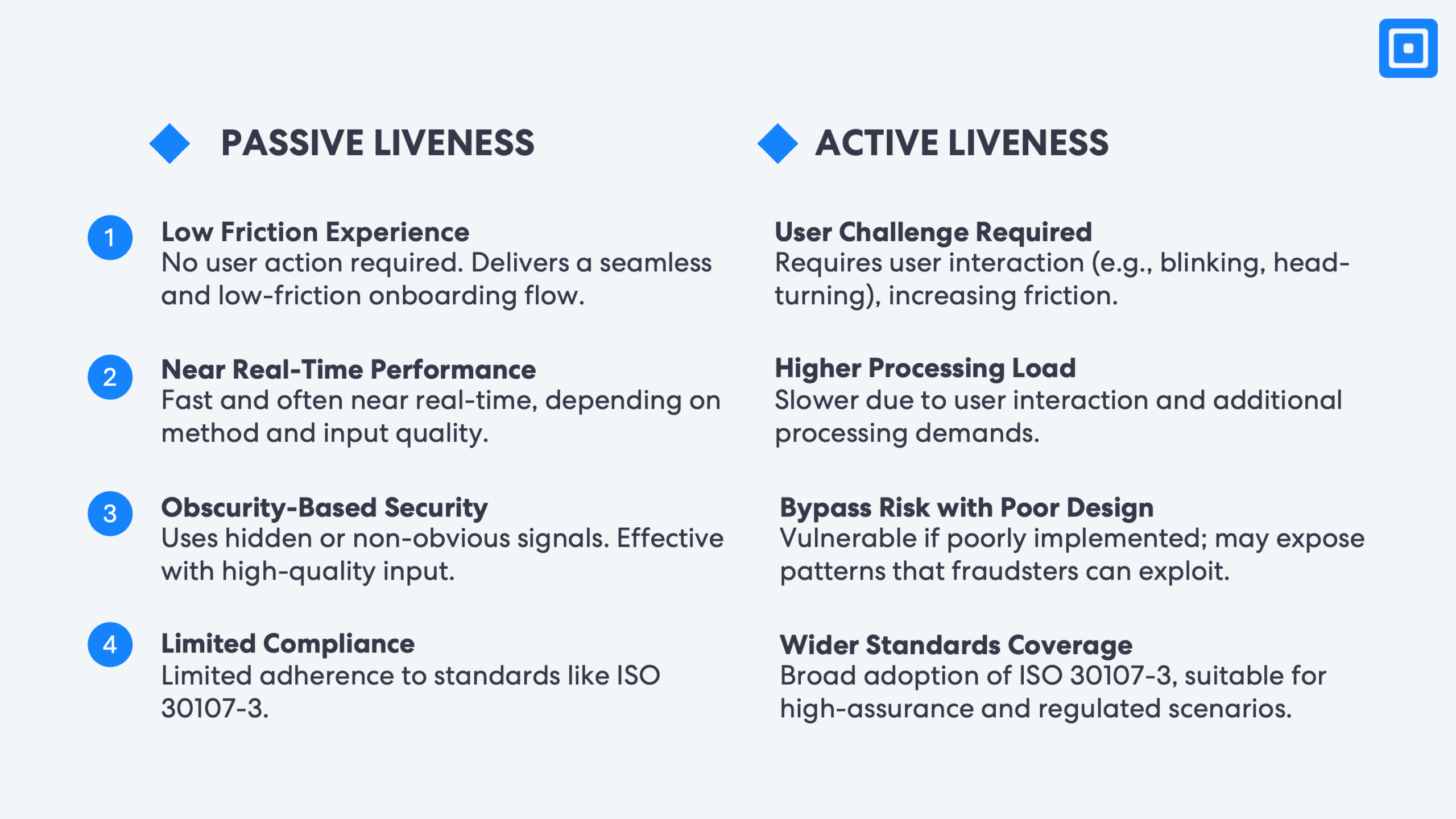
Some organisations deploy both methods depending on risk level. The application platform may use passive checks by default and switch to active biometrics when risk signals or anomalies are detected. This layered approach helps balance security, compliance, and user experience.
Both types of liveness checks help organisations detect and stop fraudulent activities by ensuring the integrity of biometric data. Neither method is universally superior. Instead, each offers protection against fraud depending on the organisation’s specific needs and risk thresholds.
Passive biometrics, in particular, can significantly enhance identity verification workflows by introducing advanced, frictionless safeguards. These solutions improve compliance, increase security, and ultimately strengthen user trust while streamlining the verification experience for both customers and businesses.
Multi-Factor Security with Biometric Checks
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) protects systems by asking users to prove who they are in more than one way. Biometric checks make MFA stronger by adding a unique trait, like a face pattern or typing style, that is hard to fake or steal. There are three main types of authentication:
Knowledge: What the user knows, like a password or PIN
Possession: What the user has, like a phone or security token
Inherence: Who the user is, like their face, fingerprint, or voice
Biometrics belong to the third group. They are always with the user and hard to copy. This makes them a strong layer in any MFA setup. Biometric MFA lowers the risk of account takeovers, helps meet compliance rules, and builds trust with users.
Both active and passive biometrics, when used together, improve flexibility. A platform might use passive checks for normal logins and switch to active checks if something unusual is detected. This helps stop fraud without slowing down trusted users.
User Experience: Balancing Security and Simplicity
Biometric checks must provide strong security without making the user journey difficult. A smooth experience helps build trust, reduce drop-off, and improve conversion rates, especially during onboarding.
Active biometrics increase assurance but require the user to perform a task. While these steps are simple, they can add time and effort. In some cases, this may cause frustration or lead users to abandon the process. On the other hand, passive biometrics offer a lower-friction option. These checks work silently in the background. As such, passive methods are well-suited for mobile apps, returning user logins, and low-risk actions.
Organisations can use both types of checks in a way that adapts to context. For instance, passive checks can run by default to keep the experience seamless. Consequently, if the system detects a risk, such as a device change or suspicious behaviour, it can trigger an active check for added certainty.
This adaptive approach helps meet security goals without slowing down the user. It also supports regulatory expectations for risk-based authentication. You can learn more here: “What is a Risk-Based Approach (RBA)?” When implemented correctly, biometric checks protect users and systems while keeping the journey fast and intuitive.
Key Takeaways
- Biometric verification uses physical or behavioural traits to confirm a user’s identity
- Liveness detection ensures the biometric input comes from a real, live person
- Active biometrics prompt the user to complete a task, such as blinking or turning their head
- Passive biometrics run in the background, analysing natural traits without user input
- Combining both methods supports adaptive risk-based authentication and fraud prevention
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Both active and passive biometric checks help verify identity and prevent fraud. Each method has its strengths, depending on whether your goal is to reduce friction or meet strict security and compliance requirements.
Active biometrics offer greater control and a higher level of identity assurance. They are best suited for high-risk situations such as digital onboarding, remote Know Your Customer (KYC) checks, or financial transactions.
Passive biometrics operate in the background without interrupting the user. They are ideal for mobile logins, returning sessions, and real-time fraud detection. These checks deliver a smooth and low-friction user experience.
The choice between active and passive methods should align with your risk appetite. The best solution is the one that fits your customer expectations and regulatory environment. Many organisations combine both methods to build a flexible system that adapts to different levels of risk and context.
Select the approach that meets your verification needs while keeping the user journey secure and seamless. To learn more about implementing active or passive biometric checks in your business, contact our expert compliance team today. These checks are increasingly mandated for secure, remote onboarding in legal, financial, and immigration sectors

Frequently Asked Questions
What is a biometric check?
Biometric checks are an identity verification method mandated by regulators for secure onboarding. These checks validate that a user is genuine by cross-referencing biological traits (such as an individual’s selfie scans) against their identity documents.
What are active and passive biometric checks?
Active biometrics require users to perform an action, such as blinking or turning their head. Passive checks work in the background, detecting liveness from motion, depth, and texture without user input. Active methods offer higher assurance, while passive methods improve convenience.
When should a business use passive biometrics instead of active?
Passive biometrics are ideal for low-friction flows such as mobile logins, app re-authentication, or fast-track onboarding. They allow verification without interrupting the user, making them effective for improving conversion rates while still detecting fraud in real time.
Are biometric checks compliant with KYC and AML regulations?
Yes. Biometric verification supports KYC and AML compliance by proving that a real person is present. ComplyCube’s solutions are designed to meet global regulatory standards, including GDPR, and are trusted by regulated industries to meet identity assurance requirements.
Can active and passive biometric checks be used together?
Yes. Many organisations use passive checks by default and escalate to active ones when risks are detected. This layered approach balances user experience with fraud prevention, adapting dynamically to context, device signals, and transaction risk levels.