Every day, millions of documents, be it passports, ID cards, or driver’s licenses, are checked for authentication purposes. Whether it’s a bank assessing the validity of a customer’s identity documents through ID verification or a government institution ensuring the integrity of its processes, document verification sustains and promotes trust in systems globally.
Reliable document checks are essential to safeguard personal identities, financial assets, and compliance posture. This guide explores the ins and outs of document checks, focusing on ID document verification, what to look for in an IDV provider, and the pivotal role such solutions play in establishing trust while preventing identity theft and fraud.
What is Document Verification?
Document verification is the process through which a business confirms the authenticity and validity of a document. It involves analyzing specific attributes of a document to confirm that it has not been altered, tampered with, or forged. Verifying the legitimacy of these documents protects businesses from potential risks and ensures adherence to Anti-money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) compliance regulations.
Technological advancements have led to significant improvements in digital document authentication systems. These solutions use advanced computer vision algorithms, Optical Character Recognition (OCR), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Machine Learning (ML) to make the document verification process quicker, more accurate, and faster.
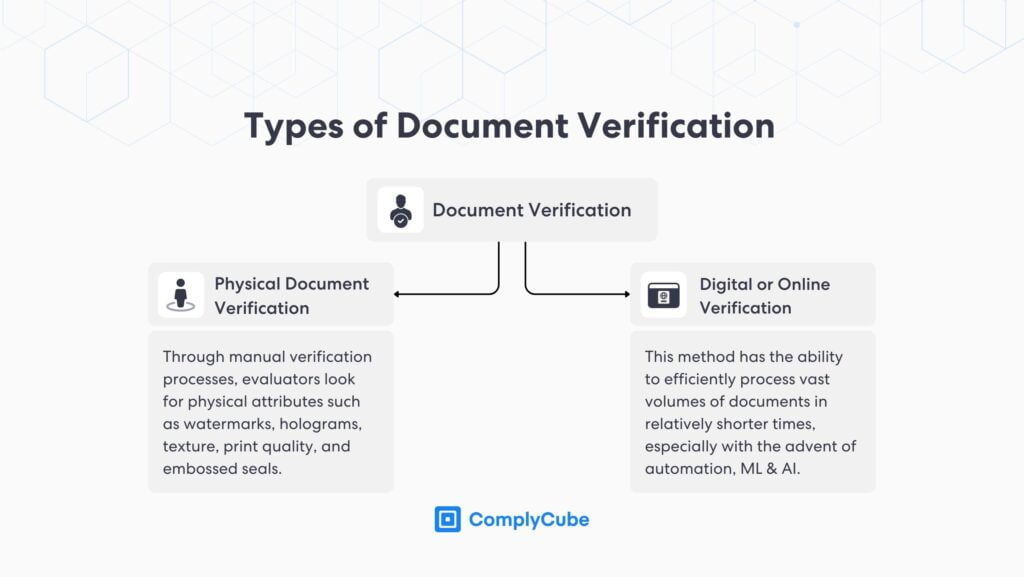
Types of Document Verification
At its core, there are two types of document verification:
Physical Document Verification involves the direct examination of hard-copy documents. Through manual verification processes, evaluators look for physical attributes such as watermarks, holograms, texture, print quality, and embossed seals. This manual review method requires trained personnel to verify documents, as the security features on many official documents are intricate.
Digital or Online Verification harnesses technologies such as OCR to read and verify content from physical documents. This method has gained popularity due to its ability to efficiently process vast volumes of documents in relatively shorter times, especially with automation, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence tools.
Common Document Checks
While document checks can be broadly categorized into physical and digital, a more granular exploration reveals specific use cases:
ID Verification: This method ensures that an individual is genuinely who they claim to be when running customer identity verification. Using photo-based identity documents such as passports, driver’s licenses, or national ID cards, it verifies an individual’s name, photo, and sometimes biometric data, ensuring a match between the information provided and the authoritative source.
Proof of Address Checks: This process analyzes an individual’s or entity’s Proof of Address (PoA) documents, such as utility bills and bank statements, to extract relevant information, match personal details against client data, and ensure the PoA document is valid. The extracted address can be cross-referenced against trusted sources using an address verification service.
Businesses might choose to verify documents for different purposes. ID verification is the main document check required across various industries to bolster trust in business interactions and promote KYC/AML compliance, especially online.

The Mechanics Behind ID Document Verification
Identity verification can be established with varying levels of assurance based on the business and industry’s regulatory environment. Depending on the desired level of identity assurance, one or more means of ID document verification can be used. Details on how these verification mechanisms work will be elaborated upon shortly.
Machine Learning and Computer Vision
Computer vision enables machines to process and understand visual data from their surroundings, mirroring human capabilities. It focuses on creating algorithms and methods that allow computers to interpret images and videos and make decisions rooted in visual observations by replicating human insights.
In the context of document validation and verification, computer vision refers to the ability of a computer system to automatically process, analyze, and interpret visual information, specifically to authenticate or validate an individual’s identity. This can involve facial recognition, document verification, liveness detection, and OCR to extract data from ID cards and other documents.

Near-Field Communication (NFC) Verification
NFC is a short-range wireless technology that allows devices to exchange data when brought into close proximity, typically within a few centimeters. It facilitates quick and easy communication between devices without needing an internet connection.
Modern ID cards and e-passports incorporate embedded RFID chips that securely hold encrypted personal details. When these chips are accessed by an NFC-capable device (scanner or smartphone), the stored data can be read and validated.
State-of-the-art verification solutions leverage the NFC mechanism to verify the digital document’s authenticity and inspect that the encoded data matches the information presented, thereby safeguarding against potential tampering and offering a streamlined means of confirming identity.

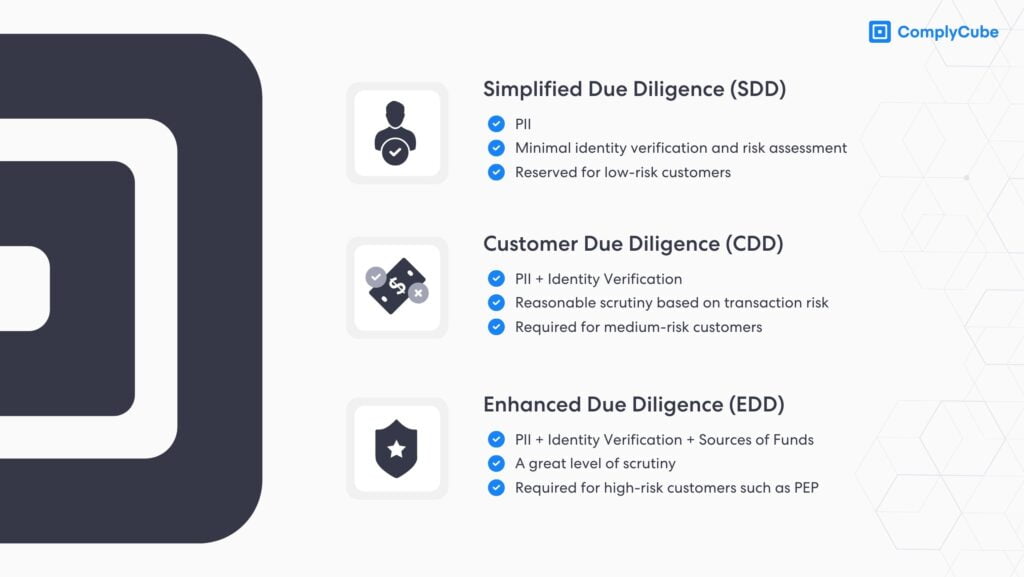
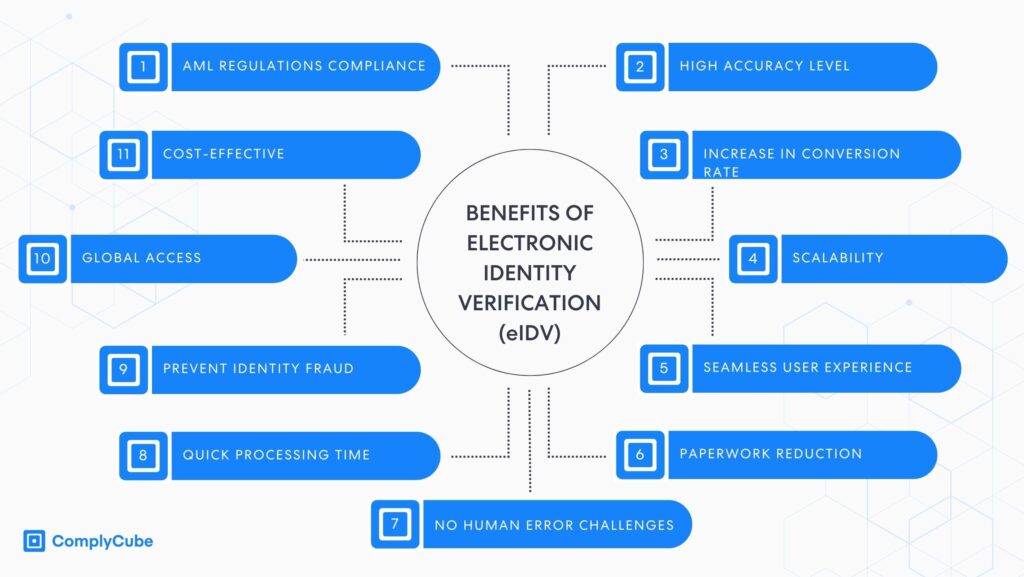
eIDV (electronic Identity Verification)
eIDV, sometimes referred to as database or KYC data checks, validates individual customer details such as name, birth date, address, and SSN by comparing them with reputable data sources, including official records, to prevent identity theft. These sources can be translated into consumer reporting agencies, credit bureaus, utility records (such as phone or electricity bills), and official government databases.
In specific regions and applications, regulatory bodies mandate a “2+2 check” to verify the identity of customers. This requires that a minimum of two customer attributes align with two distinct data sources.
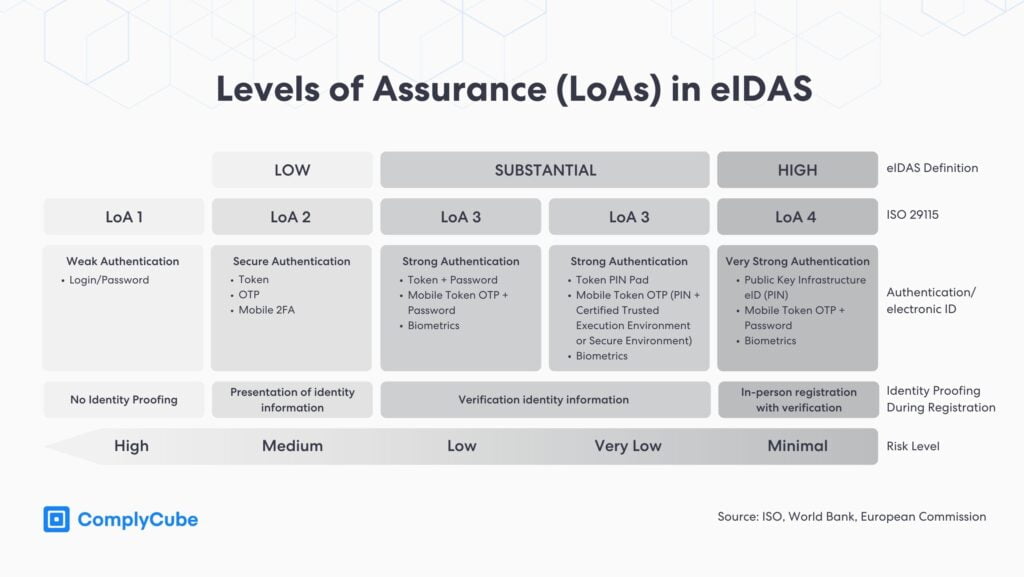
Levels of Assurance (LoAs) in eIDAS
Digital Identity in Europe, predominantly represented by electronic identification (eID), is crucial for accessing online services, electronic signatures, and authentication. Trust in these digital transactions hinges on the Level of Assurance (LoA), which measures the confidence in a digital identity’s accuracy and reliability.
The EU’s eIDAS framework defines three primary LoA tiers, benchmarked against the ISO 29115 standard:
Low: Offers a moderate confidence level, typically relying on single-factor authentication.
Substantial: Requires at least two authentication factors and verified identity information.
High: Demands two authentication factors and robust safeguards against identity tampering.
When accessing sensitive government platforms, claiming social security benefits, or filing taxes online, a High Level of Assurance (LoA) is essential. In these scenarios, stringent checks, often including the thorough verification of physical identity documents, ensure that only the legitimate individual can make critical updates or claims. For activities like purchasing a prepaid SIM card from a telecom company, a Low LoA might suffice, although some countries now require IDV for this service.
Recent research from December 2022 indicates a notable trend towards eID schemes with Substantial and High LoAs, accounting for 90% of all schemes.
When is Document Verification Required?
Document verification is integral to various processes across industries, such as banking, financial services, healthcare, recruitment, and more, due to the stringent requirements of AML and KYC regulations. These rules are enforced to combat financial fraud, money laundering, and terrorist financing.
Intergovernmental and regulatory bodies safeguard the integrity of nations and counteract criminal activities such as fraud and terrorist financing. Financial institutions have to conform to rigorous regulations such as the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and US Patriot Act, while businesses across different sectors have to abide by guidelines recommended by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and the EU Directives (including financial services companies).
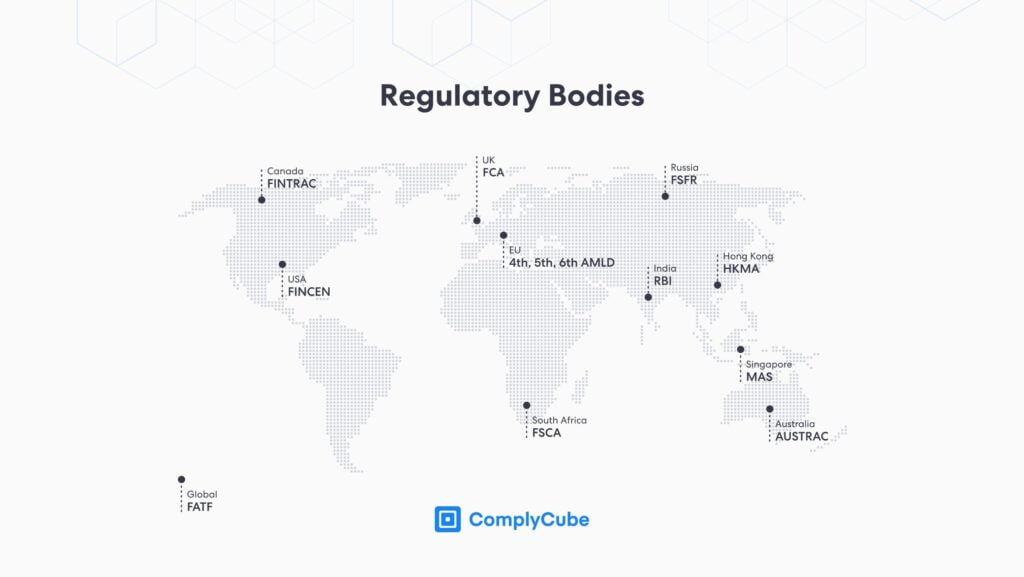
To adhere to the regulations and guidelines encompassed by the KYC framework, businesses must conduct document verifications at various points throughout the customer’s journey, such as:
Customer Identification Program (CIP): The minimum requirements for a customer onboarding process, enabling businesses to reasonably ascertain the genuine identity of every customer. Under Section 326 of the US Patriot Act, the program includes proper identification of the individual or entity opening the account, recordkeeping, and corroboration with governmental lists.
Ongoing Due Diligence (ODD): Rather than a one-time check, it’s an active effort to ensure that customer profiles remain accurate, relevant, and compliant with evolving regulations. This proactive continuous monitoring approach helps companies identify and address potential risks, ensuring they maintain integrity and trust in their operations.
How Does Online Document Verification Work?
Amidst evolving financial regulations, the foundation of trust between businesses such as financial institutions and their customers largely hinges on stringent identity verification measures. Central to ensuring this trust is the online ID document verification process, a structured approach to authenticating users in line with AML and KYC protocols.
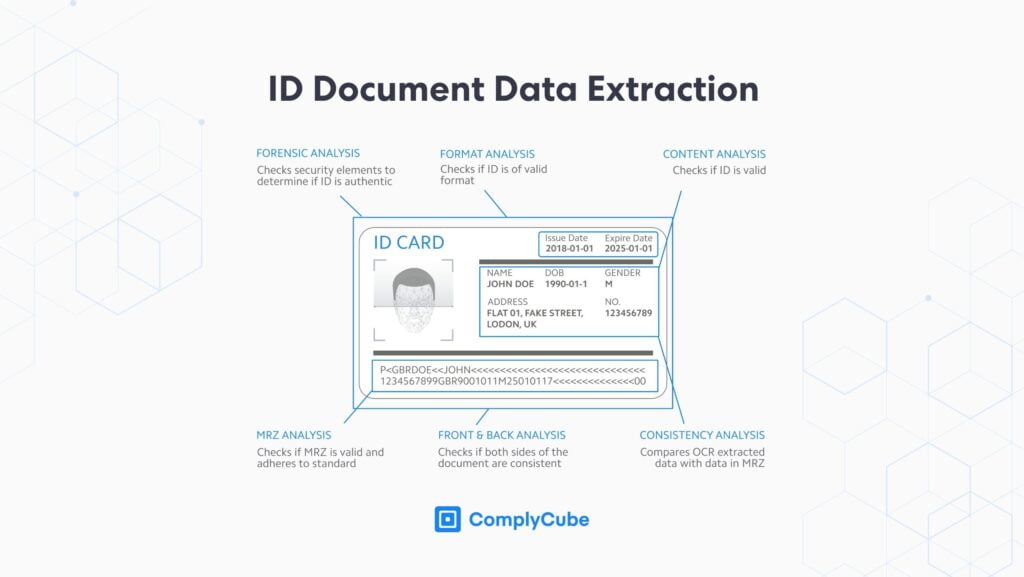
Identity Document Data Extraction
Businesses generally integrate document verification solutions on account opening to confirm data integrity and spot fraudulent documents. An effective AI-powered verification system supports a broad range of country and ID combinations, such as a passport, driver’s license, identity card, residence permit, travel document, and other government-issued IDs from around the world. At times, more documents, such as bank statements or utility bills, are required when further investigation is needed.
Data extraction is completed using digital imaging or scanners. With the help of OCR, the image text is converted into machine-readable characters. The identity verification software will extract all the available data from fields such as the Visual Inspection Zone (VIZ), Machine Readable Zone (MRZ), and barcodes to verify identity documents.
Data Validation
State-of-the-art AI, machine learning, and advanced analytics allow businesses to perform various types of analysis on ID documents, including detailed checks on visual security elements, potential tampering or manipulation, document liveness, and blacklist checks.
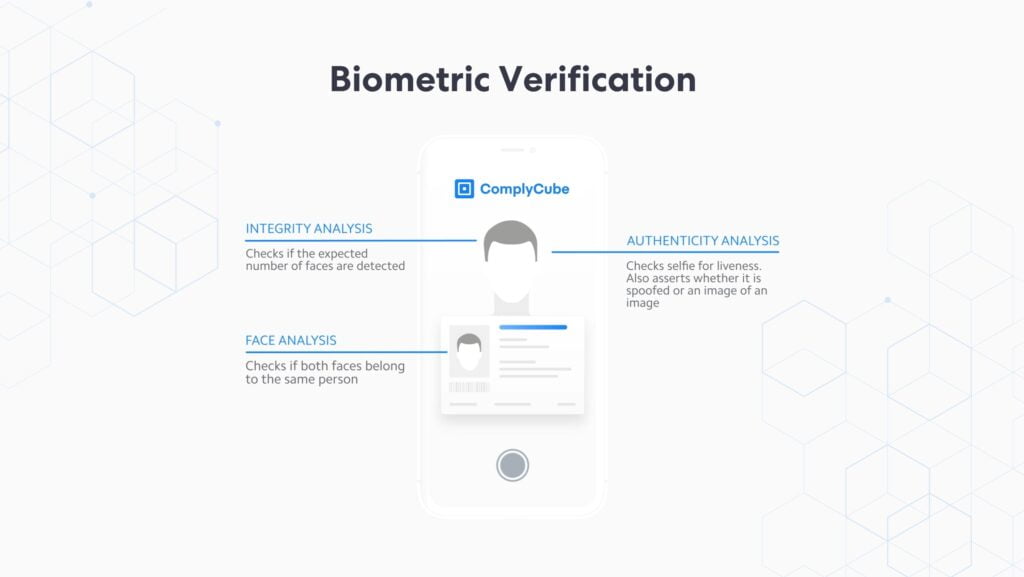
Biometric Verification
Some platforms go a step further in the IDV journey by requiring users to submit a live photo or video at different stages, such as customer onboarding. Biometric algorithms compare the facial biometrics live data to the photo on the ID to ensure the person presenting the ID is the same person. Anti-spoofing detection safeguards businesses from sophisticated presentation attacks like 3D masks without introducing additional user friction.
You can learn more about the topic here: The Advantages of Biometric Authentication.
Manual Checks (Optional)
Some companies integrate manual checks when verifying documents. IDV specialists might use manual document verification processes to review the security features of official papers that raise flags or don’t pass automated checks. The element of human intuition and judgment acts as a safety net. However, it is optional if an effective document authentication software is employed, as human error can become a challenge if the person verifying the identities of new customers does not have the necessary training and knowledge.
Verification Results and Further Action
Provided that the government-issued ID document used, such as a driver’s license or passport, is verified successfully, the user can proceed with the account creation. If there are discrepancies or the verification fails, the user may be asked to retry or provide additional documentation, such as a utility bill or bank statement. In the case of an application that triggers an alert, the compliance team is notified so that they can run an enhanced due diligence (EDD) process to investigate further.
You can learn more about the topic here: Navigating the World of Enhanced Due Diligence.
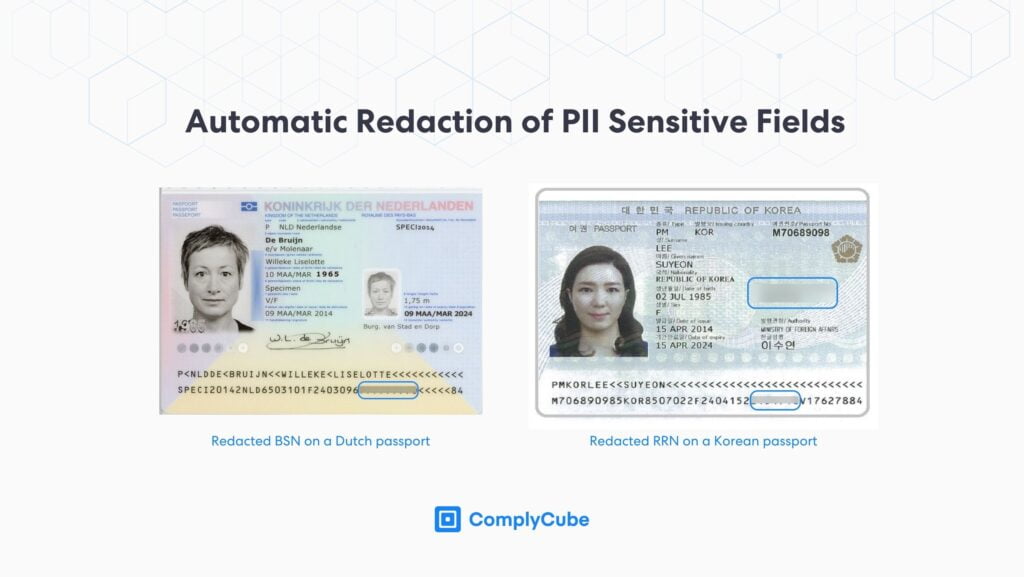
Data Storage and Protection
Platforms that store user data must ensure that this sensitive information is stored securely, often using encryption and adhering to local data and privacy protection regulations such as the GDPR, UK GDPR, CCPA, and more. For robust compliance measures, leading document authentication software redact or mask sensitive fields to adhere to global privacy laws. Sensitive fields, among others, include:
Korean RRN (Resident Registration Number)
Singaporean NRIC (National Registration Identity Card Number)
Dutch BSN (Burgerservicenummer or Dutch Citizen Service Number)
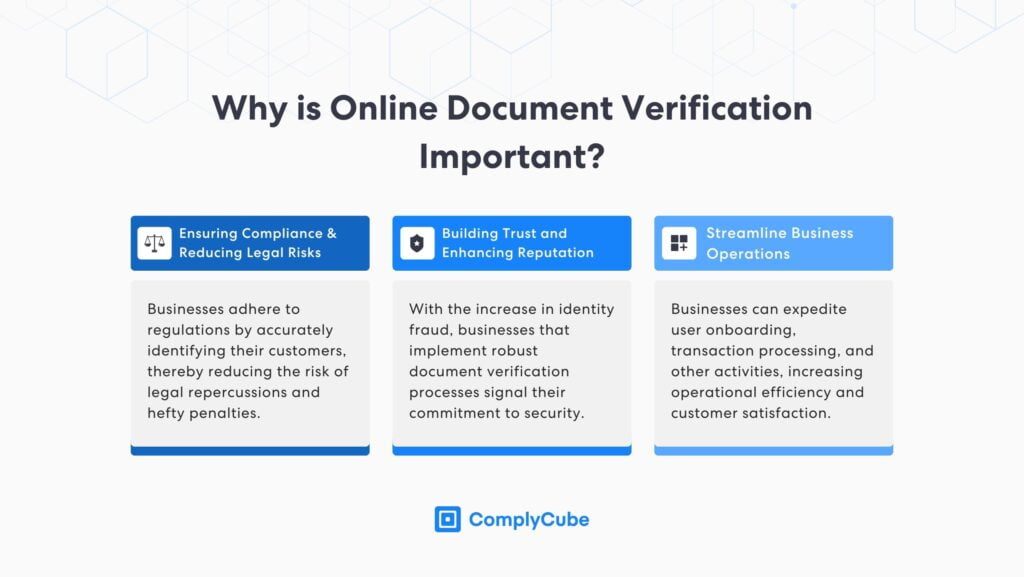
Why is Online Document Verification Important?
As more businesses shift to the online environment, the risk of encountering forged or counterfeit documents surges. Online document verification has become an essential tool to instill trust and prevent identity theft in this vast digital marketplace.
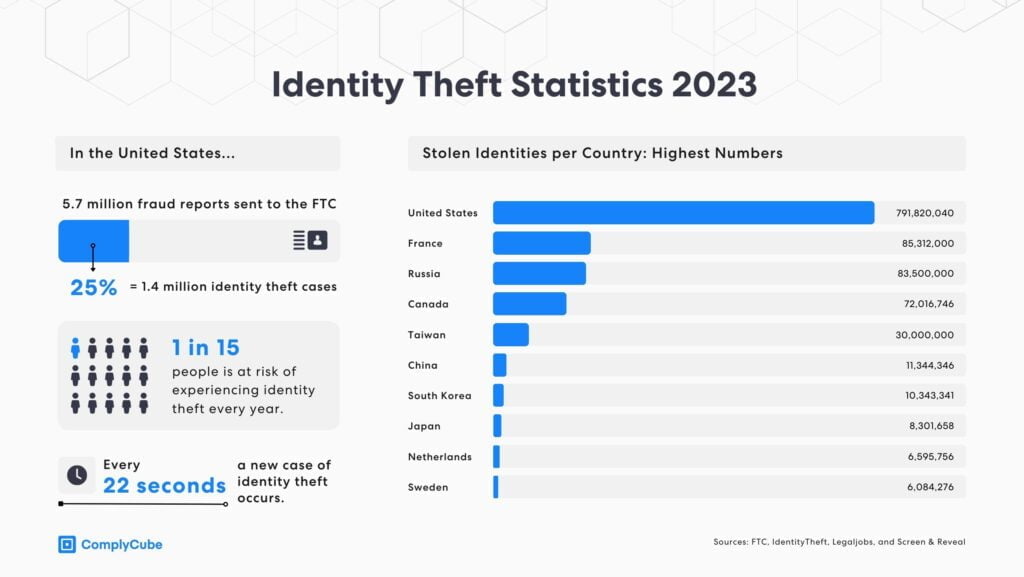
When combining figures from traditional identity fraud with scams, the total financial toll amounted to $52 billion, impacting 42 million consumers in the US alone, accordning to Javelin’s 2022 Identity Fraud Study.
In essence, document verification is not just a procedural necessity but a strategic tool that brings about a hefty number of benefits, including:
Ensuring Compliance and Reducing Legal Risks: Businesses adhere to regulations by accurately identifying their customers, thereby reducing the risk of legal repercussions and hefty penalties.
Building Trust and Enhancing Reputation: With the increase in identity fraud, businesses that implement robust document verification processes signal their commitment to security.
Streamlining Business Operations: Businesses can expedite user onboarding, transaction processing, and other activities, increasing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Document Verification Challenges: Evolving Fraud Techniques
Navigating the intricacies of document verification presents a host of challenges for businesses. These challenges not only pertain to the technical aspects but also involve operational, regulatory, and cultural factors.
As verification technologies become more sophisticated, so do the methods employed by fraudsters. From high-quality forged documents to deepfake videos and images, malicious entities are continuously finding new ways to bypass standard verification checks. This constant game of cat and mouse requires verification systems to be agile and adaptive.
In North America, there was a significant rise in the occurrence of deepfakes from 2022 to Q1 2023. Specifically, the US saw an increase from 0.2% to 2.6%, while in Canada, the rate leapt from 0.1% to 4.6%.
A significant instance of online ID fraud occurred in 2020 when an individual employed multiple accounts, counterfeit driver’s licenses, and wigs to deceive the digital identity verification platform used by US government agencies. According to reports, $900,000 was claimed on unemployment grounds before the scam was detected and halted. The intended target of this scheme was to secure $2.5 million unlawfully.
To prevent similar cases and mitigate fraud, IDV providers implement document liveness detection. The process typically refers to methods used to determine if a document (such as an ID card or passport) is genuine and not a reproduction or a stolen, expired, or digitally manipulated image.
Document liveness checks use machine learning and sophisticated algorithms to analyze different elements of the ID document, such as holograms, stamps, coat of arms, expiration/issuance date, 3D properties, and more based on the document type.

How to Choose the Right ID Document Verification Software?
Selecting a reliable ID document verification software is the best way to ensure compliance, security, and a seamless user experience. Here’s a brief cheat sheet for choosing the right solution:
Determine the Company’s Needs
Define your company’s needs based on your business model and in line with your AML/KYC risk-based approach. Then choose an ID document verification provider that allows you to quickly customize the solution according to your company’s ever-changing AML framework.Check for Multi-Modal Verification
In the age of sophisticated fraud, having multi-modal verification such as OCR, NFC, biometric checks, and liveness detection is invaluable. These multi-layered checks provide a higher level of assurance, reducing the risk of accepting forged or manipulated documents for online businesses.Prioritize Rule-based Automation
An effective IDV solution streamlines operations by enabling businesses to establish distinct rules, case management processes, and thresholds. This time-effective approach ensures the team can redirect their focus to value-add tasks, optimizing overall performance.Evaluate Integration Capabilities
A robust document verification software should offer a suite of Low/No-Code solutions, robust API, Mobile SDKs, Client Libraries, and seamless CRM integrations. Ease of integration can save time, reduce operational costs, and enhance user experience.Prioritize User Experience
While security and compliance are paramount, ensuring the verification process is user-friendly is equally necessary. Lengthy or complicated flows can lead to customer frustration. Opt for software that offers an intuitive interface, minimizing friction and maximizing user retention.Review Support & Compliance Updates
Regulations and industry standards evolve. It’s crucial to select a software provider that runs regular updates in line with regulatory changes and requirements. Additionally, having strong customer support ensures that any issues or queries get resolved promptly, ensuring smooth operations.

The Future of Document Verification
As we look ahead, the landscape of document verification is poised for significant transformation, driven by both technological advancements and shifting global dynamics. AI and ML are anticipated to play even more central roles in online document verification and beyond. These technologies will improve accuracy rates, minimize human error, significantly reduce false positive rates, and promote fraud prevention.
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, it promotes a further surge in cross-border transactions and global operations. This could translate into a universal or standardized document verification system, fostering collaboration between nations and industries.
While the future of document verification looks bright, filled with technological innovations that promise heightened security and efficiency, the journey will require constant vigilance, adaptation, and collaboration across industries and governments.
Conclusion
Ensuring the authenticity of documents in the modern business landscape is no small task, but it’s undeniably crucial. As deceptive practices grow increasingly intricate, the imperative for robust online document verification measures rises concurrently.
By ensuring the authenticity and integrity of documents, organizations shield their reputation and enhance their operational fortitude. With cutting-edge technologies, consistent revision of verification strategies, and a steadfast commitment to global regulatory standards, enterprises can position themselves at the forefront of security and trust.
Moving into the future, it becomes evident that a flexible, comprehensive, and efficient way to conduct document verification will serve as a foundational pillar for offering a seamless customer experience, establishing trust, and maintaining seamless operations in an interconnected world.
Looking for a global compliance platform for document checks? Get in touch with us today!